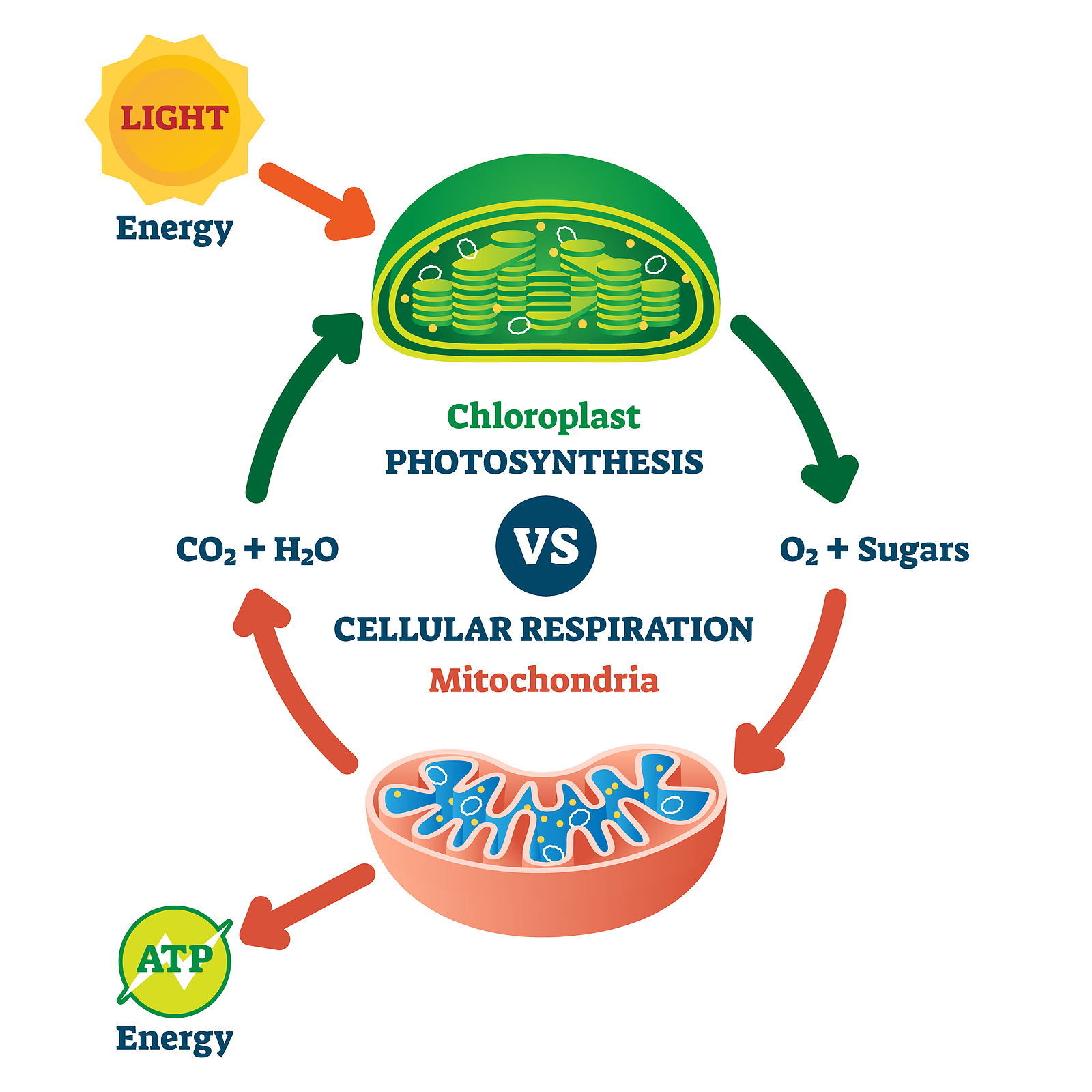
Eukaryotic autotrophs, such as plants and algae, have organelles called chloroplasts in. Web in the last video we learned a little bit about photosynthesis. Decreasing the duration of light. In a process driven by light energy, glucose molecules (or other sugars) are constructed from water and carbon. Most living things depend on photosynthetic cells to manufacture the complex organic molecules they require as a source of energy.
Photosynthesis is powered by energy from sunlight. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars. Web if you want to learn how photosynthesis works, the following sections explain the process clearly. Web photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food.
Web plants, algae, and some unicellular organisms do photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is powered by energy from sunlight. It allows energy from the sun to be converted into a storable form, usually glucose, which plants. Web summarize the overall purpose of photosynthesis, as well as its inputs and outputs. Web • photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, some other protists, and some prokaryotes.
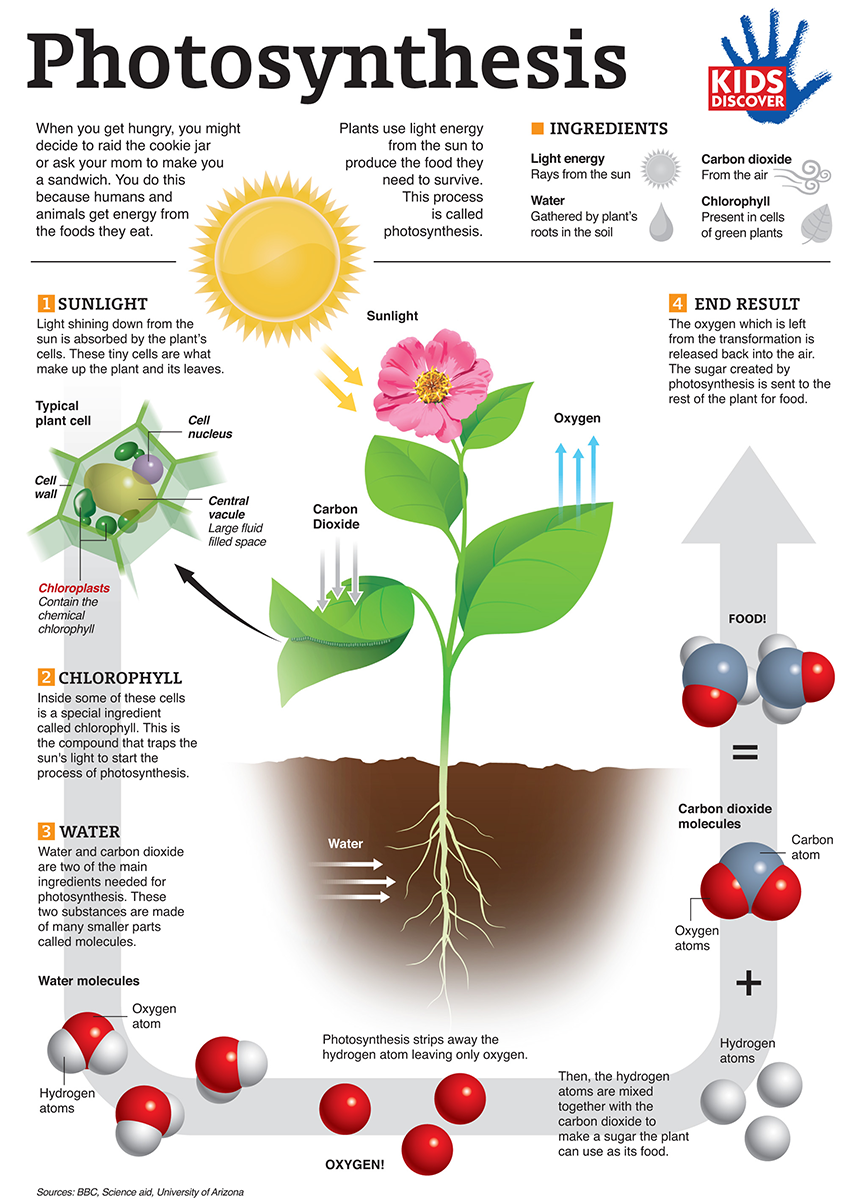
Here you will also learn how to draw a photosynthesis diagram or choose one from the available templa. • harvest energy from oxidizing inorganic substances, such as sulfur and ammonia. Web summarize the overall purpose of photosynthesis, as well as its inputs and outputs. Unit 4 elements of life. Unit 9 more about membranes. The word ‘photosynthesis’ is derived from the greek word phōs, meaning ‘light’ and synthesis meaning ‘combining together.’. Web photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars. Photosynthesis is powered by energy from sunlight. Chlorophyll absorbs the light energy from the sun to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Web plants, algae, and some unicellular organisms do photosynthesis. Unit 6 structure of a cell. Web photosynthesis, a process vital for life, involves two main stages: And we know in very general terms, it's the process where we start off with photons and water and carbon dioxide, and we use that energy in the photons to fix the carbon. The set of wavelengths that a pigment doesn't absorb are reflected, and the reflected light is what we see as color. Web in the last video we learned a little bit about photosynthesis.
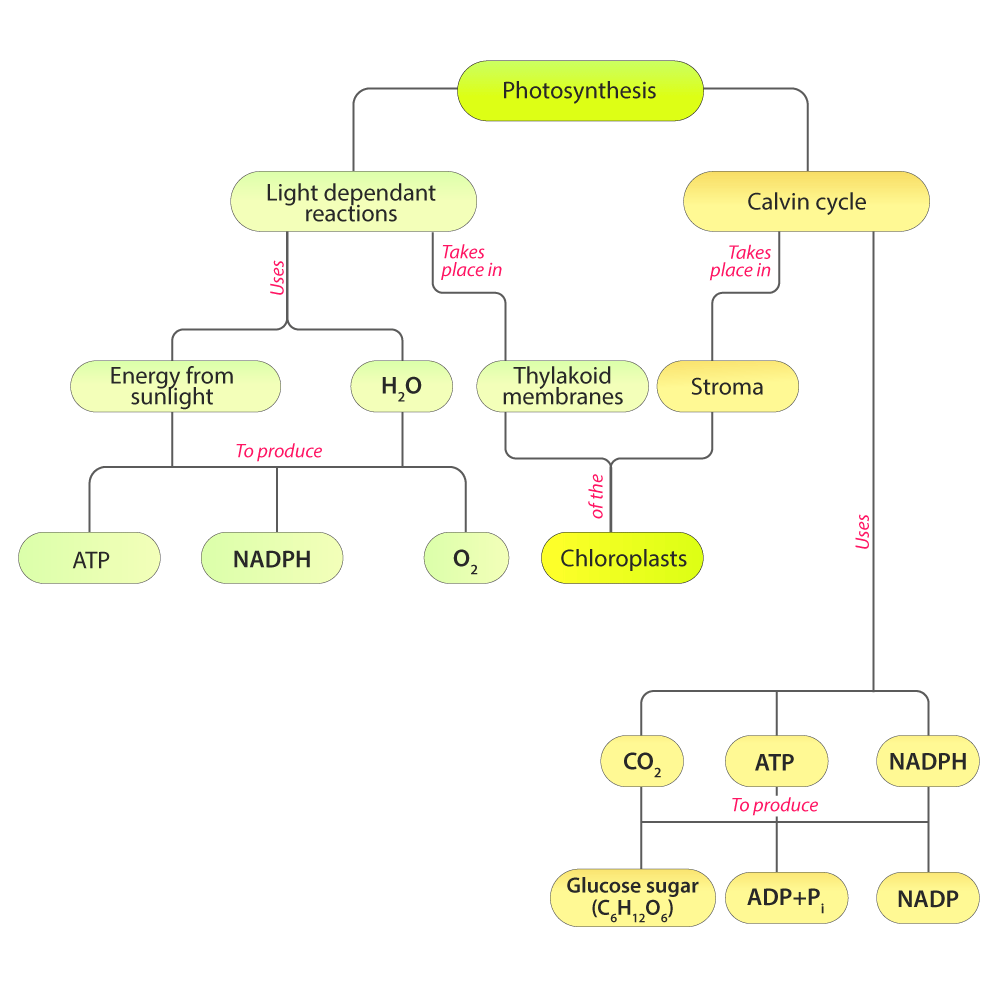
Describe The Main Components Of The Light Reactions And Calvin Cycle, And.
Unit 5 energy and enzymes. Decreasing the duration of light. Decreasing the intensity of light. Heterotrophs (=consumers) • live on organic compounds produced by other organisms.
Most Living Things Depend On Photosynthetic Cells To Manufacture The Complex Organic Molecules They Require As A Source Of Energy.
Web photosynthesis is the process by which plants make their own food. Web in the last video we learned a little bit about photosynthesis. Web in the diagram below, you can see the absorption spectra of three key pigments in photosynthesis: Eukaryotic autotrophs, such as plants and algae, have organelles called chloroplasts in.
Unit 9 More About Membranes.
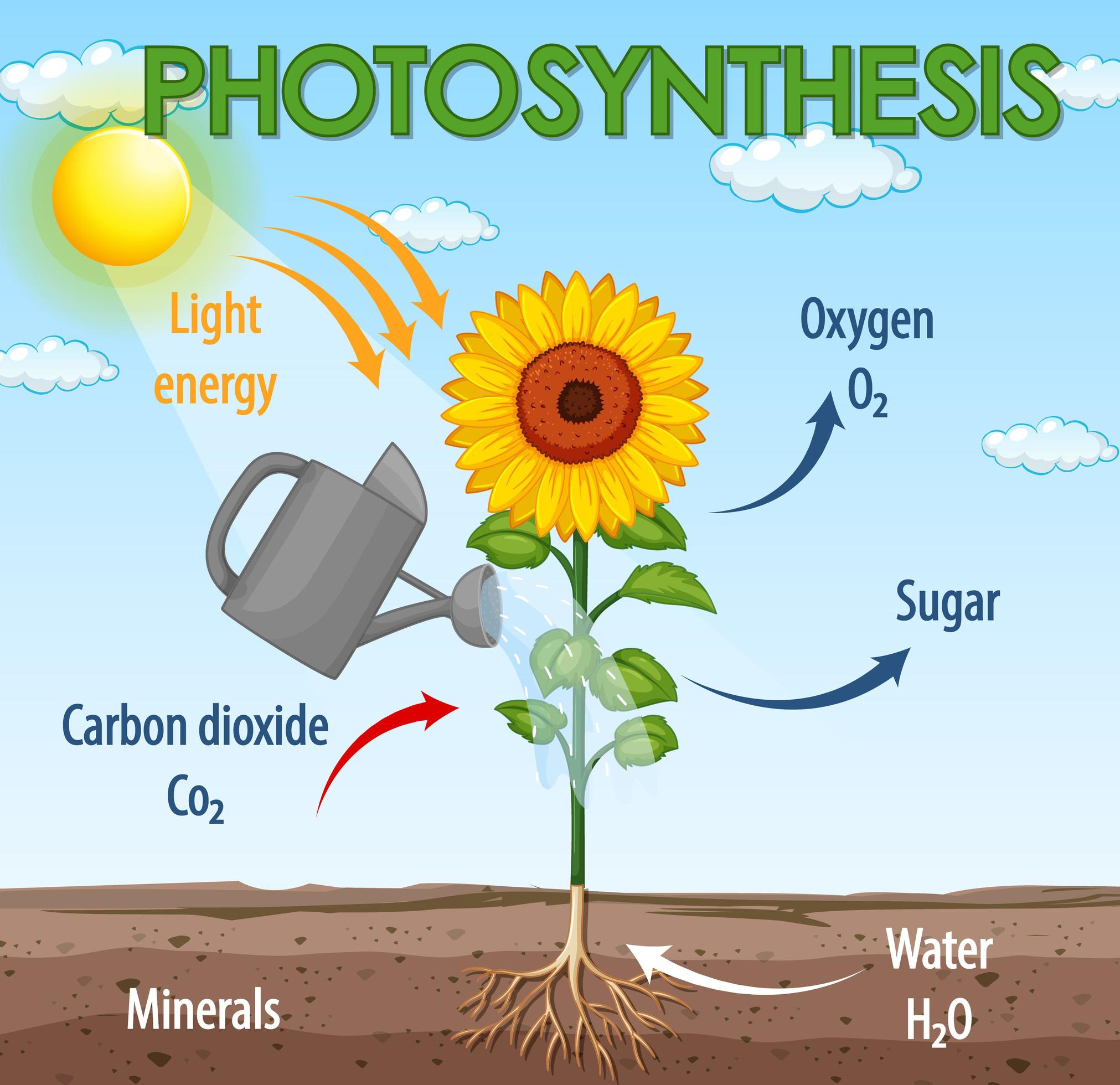
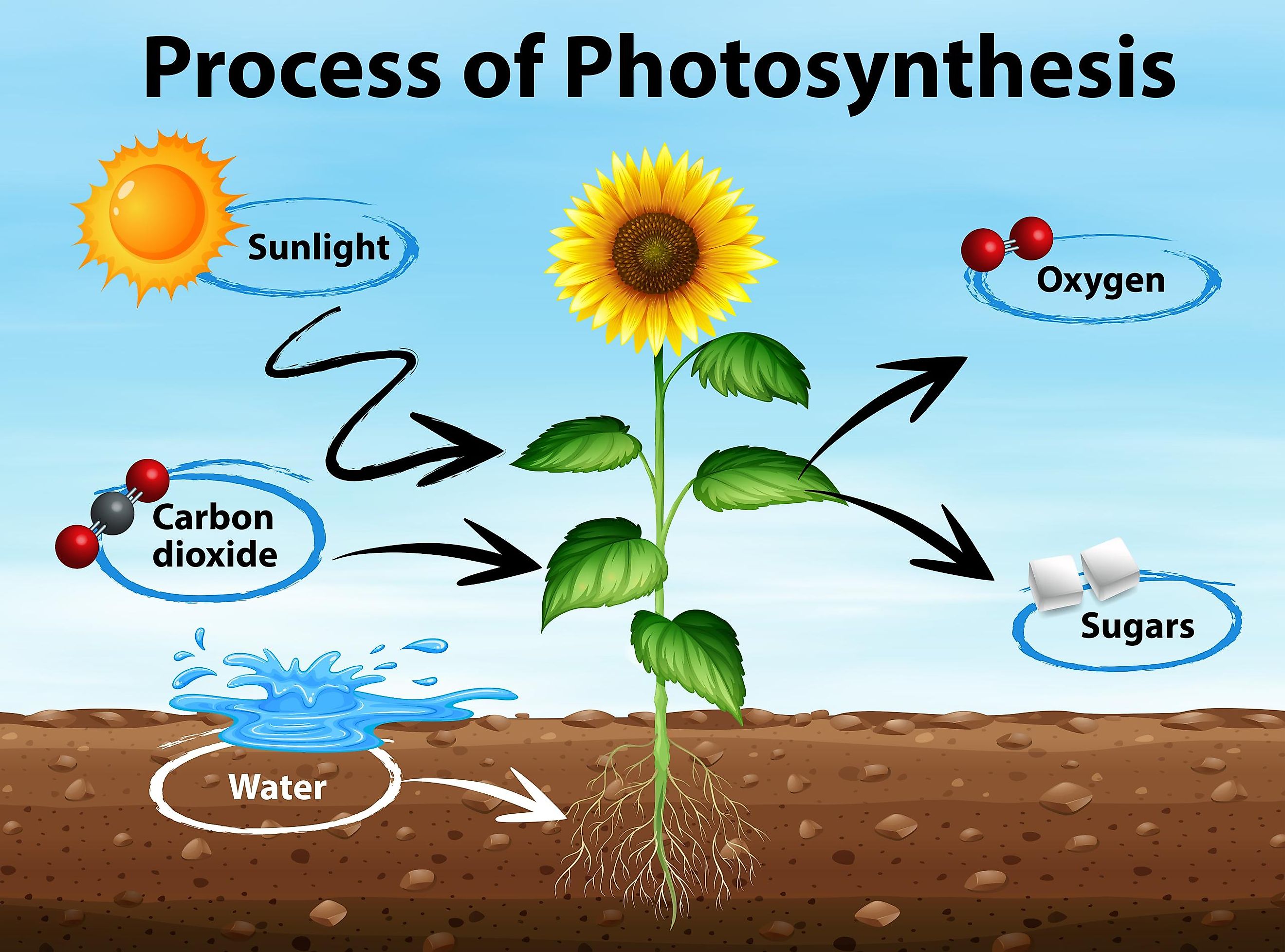
Increasing the amount of oxygen. Web this article will introduce the process of photosynthesis, how it works, and how to draw a flowchart to represent the workflow inside the plant when photosynthesis happens. Web summarize the overall purpose of photosynthesis, as well as its inputs and outputs. This energy is used to rearrange atoms in carbon dioxide and water to make oxygen and sugars.
Here You Will Also Learn How To Draw A Photosynthesis Diagram Or Choose One From The Available Templa.
Describe the structures used to perform photosynthesis in plants. Web photosynthesis uses carbon dioxide and water to assemble carbohydrate molecules (usually glucose) and releases oxygen into the air. Web photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and certain other organisms transform light energy into chemical energy. Web photosynthesis is the process in which light energy is converted to chemical energy in the form of sugars.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-944092980-819822c860ac4b1bb4c4b3a5170878ac.jpg)
![[Class 7] Photosynthesis Process, Steps, and Important questions](https://d77da31580fbc8944c00-52b01ccbcfe56047120eec75d9cb2cbd.ssl.cf6.rackcdn.com/88ebb57f-91eb-4d9a-a7a3-64252e5f3b21/photosynthesis---teachoo.jpg)