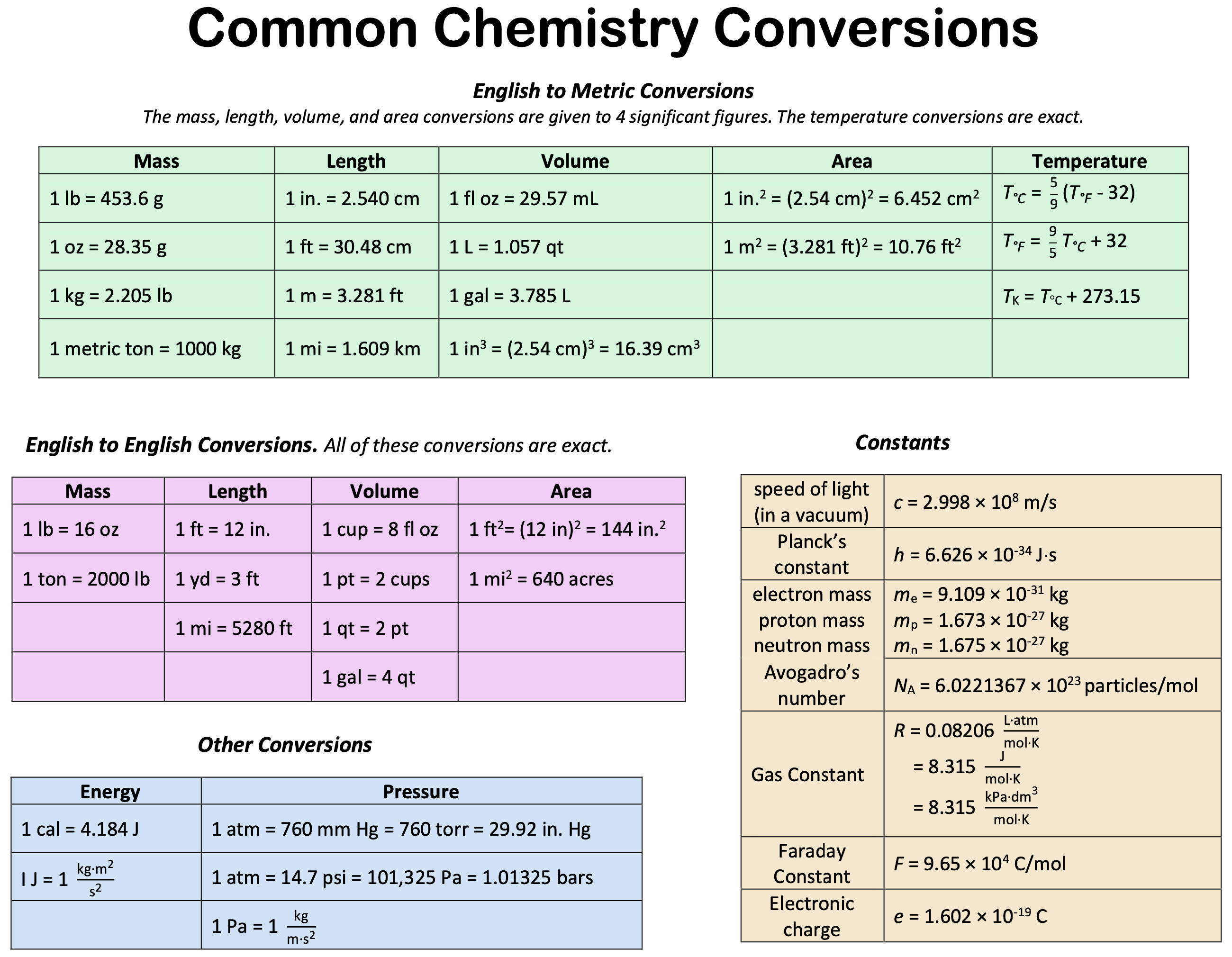
[ (% × d) / mw] × 10 = molarity. Consider mercury, which is a liquid at room temperature and has a density of 13.6 g/ml. Learn how to do chemistry unit conversions and review the most common units of measurement and conversion factors. A simple conversion factor can convert meters into centimeters, or a more complex one can convert miles per hour into meters per second. Web si and metric measurement systems.
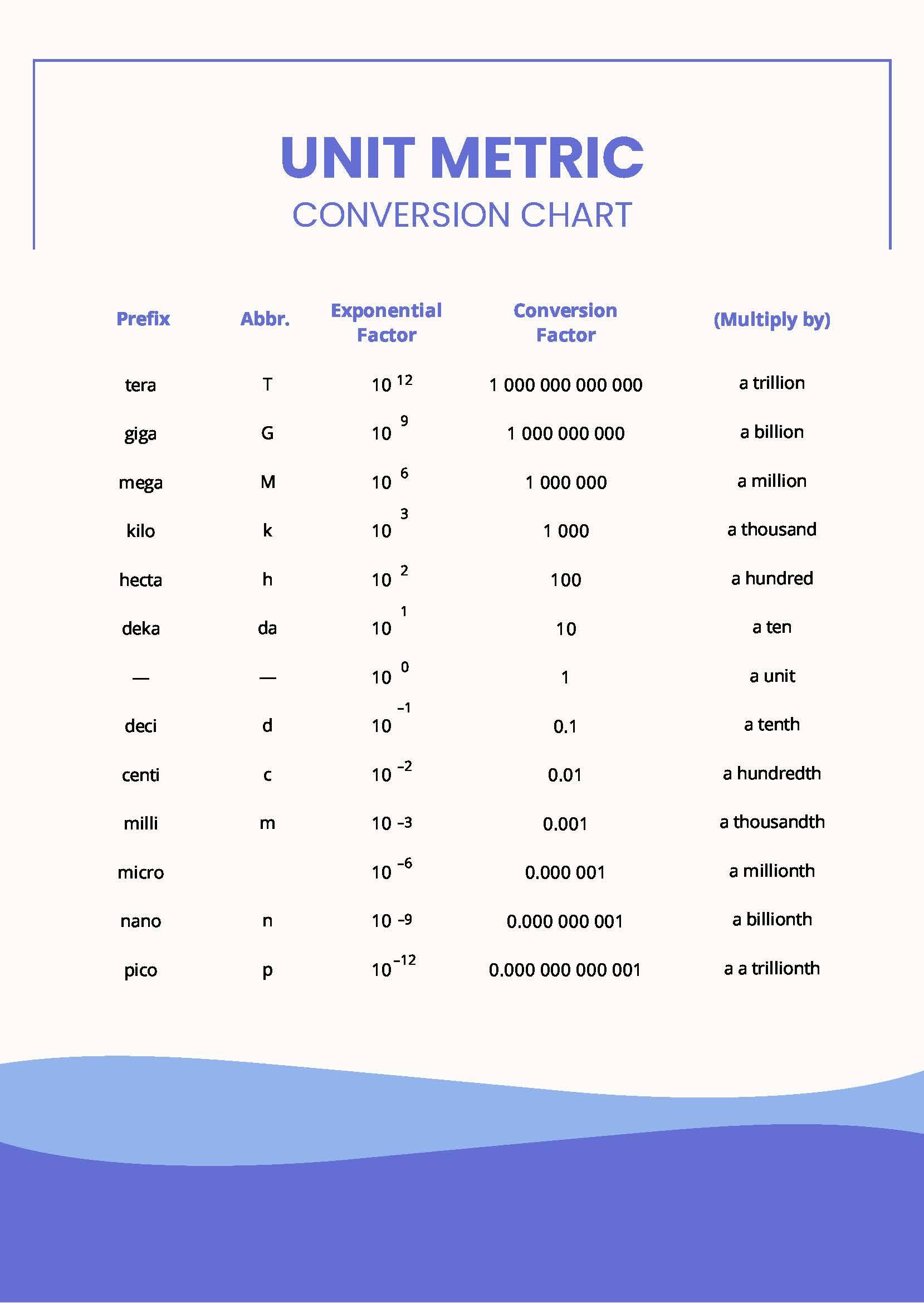
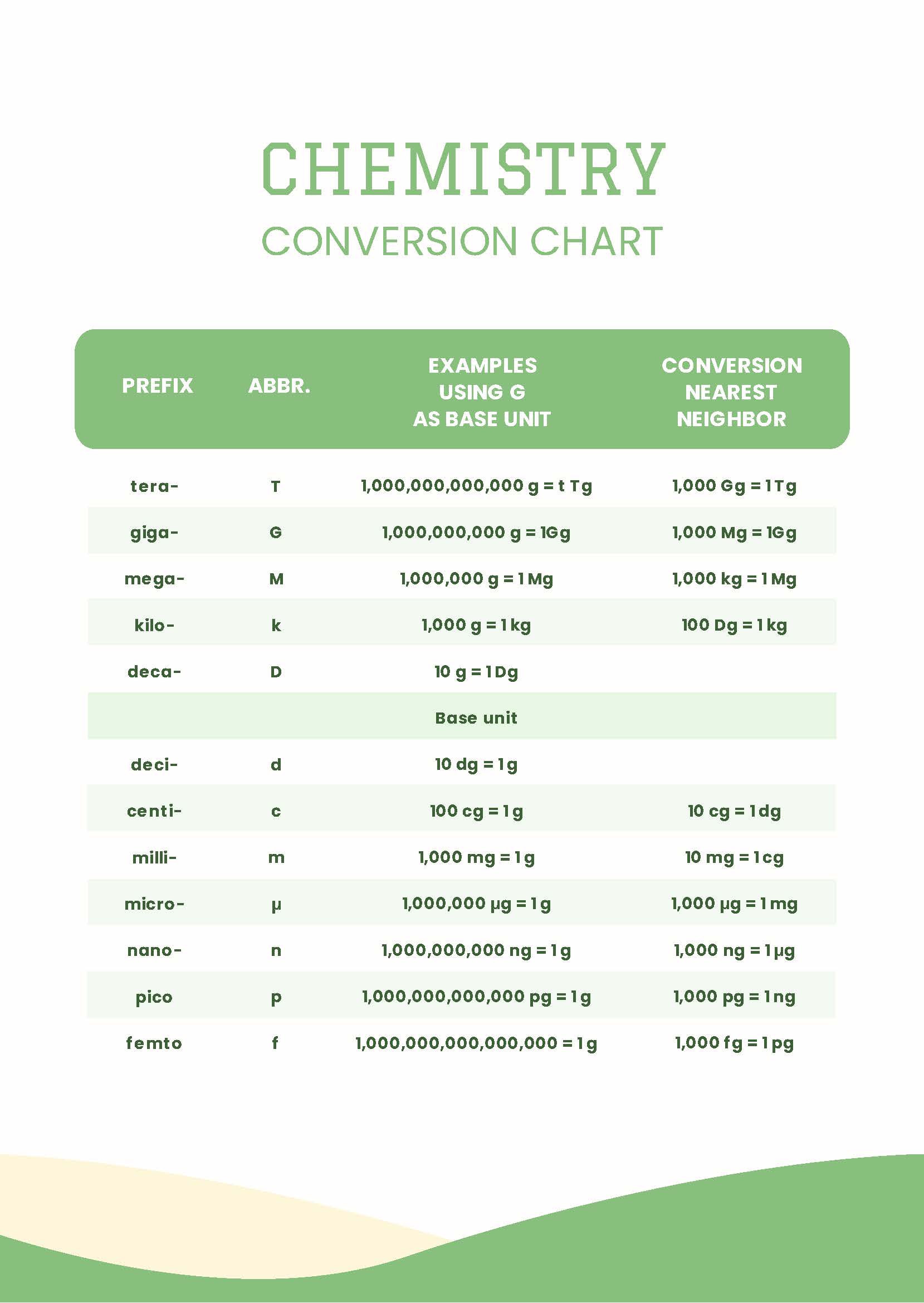
At this temperature, the conversion factor is the one provided in this table. For example, the lengths of 2.54 cm and 1 in. These reference tables show the different bases and prefixes used to designate metric units with the si system. For example, density can be used to convert between the mass and the volume of a substance. The only difference is the conversion factor used.
Click on a quantity name above to access the unit converter. Web unit converters (aka unit calculators) are tools that allow to convert between different units of measurement for the same quantity. The following table includes some useful conversion factors. Web therefore, the exact relationship of btu to joules and other energy units depends on the temperature at which btu is measured. D = density (or specific gravity);
Consider mercury, which is a liquid at room temperature and has a density of 13.6 g/ml. 1 lb = 453.6 g. This is the most complete collection of unit converters with 39 different physical quantities supported. We write this on the left side of an equals sign. Web the conversion relations in this table are commonly used to equate masses and weight assuming a nominal value for g at the surface of the earth. 59 °f (15 °c) is the most widely used reference temperature for btu definition in the united states. Units in the first column are generally not used in nist publications except those that are italicized. The basic unit of mass (weight) is: 59 °f (15 °c) is the most widely used reference temperature for btu definition in the united states. Web c si units and conversions. At this temperature, the conversion factor is the one provided in this table. 1 in = 2.540 cm. [ (% × d) / mw] × 10 = molarity. Mw = molecular weight (or formula weight). The base units are defined for measurable properties and the prefixes describe varied sizes of units within each base unit.
59 °F (15 °C) Is The Most Widely Used Reference Temperature For Btu Definition In The United States.
Web the following equation is used for calculating acid and base molarity where the concentration is given in wt %: Web english to metric conversions. The only difference is the conversion factor used. See the conversion factor chart.
The Basic Unit Of Length Is:
Web the first step in the procedure is to identify the unit for the value we want to calculate. The base units are defined for measurable properties and the prefixes describe varied sizes of units within each base unit. Bold values indicate exact conversion values. Web conversion factors can also be constructed for converting between different kinds of units.
The Above Equation Can Then Be Used To Calculate The Molarity Of The 70 Wt % Nitric Acid:
The following are some of the prefixes for the metric system. The following table includes some useful conversion factors. At this temperature, the conversion factor is the one provided in this table. 2 btu is the amount of energy needed to heat one pound of water by one degree fahrenheit.
[ (% × D) / Mw] × 10 = Molarity.
Web basic conversion cheat sheet. Below is a table of conversion factors. A simple conversion factor can convert meters into centimeters, or a more complex one can convert miles per hour into meters per second. Learn how to do chemistry unit conversions and review the most common units of measurement and conversion factors.