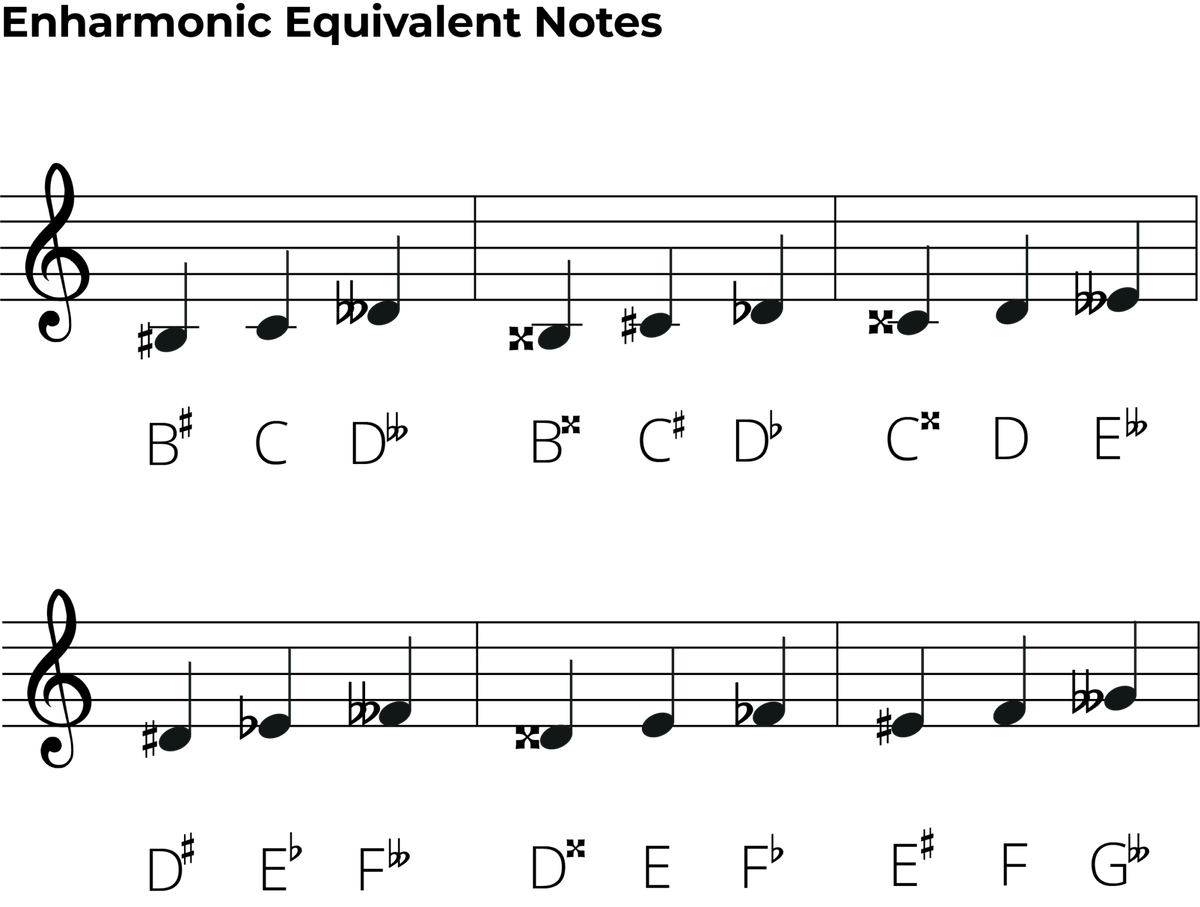Web an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, chord or key signature that sounds the same as other note, interval, chord or key signature but is named differently. Have you ever wondered why some notes on the piano have the same name? Here is a handy guide to the intervals of all twelve keys. Web in a nutshell, the term enharmonic equivalent means notes that sound the same as one another but are named or “spelled” differently. A sharp symbol raises a pitch by one half step.
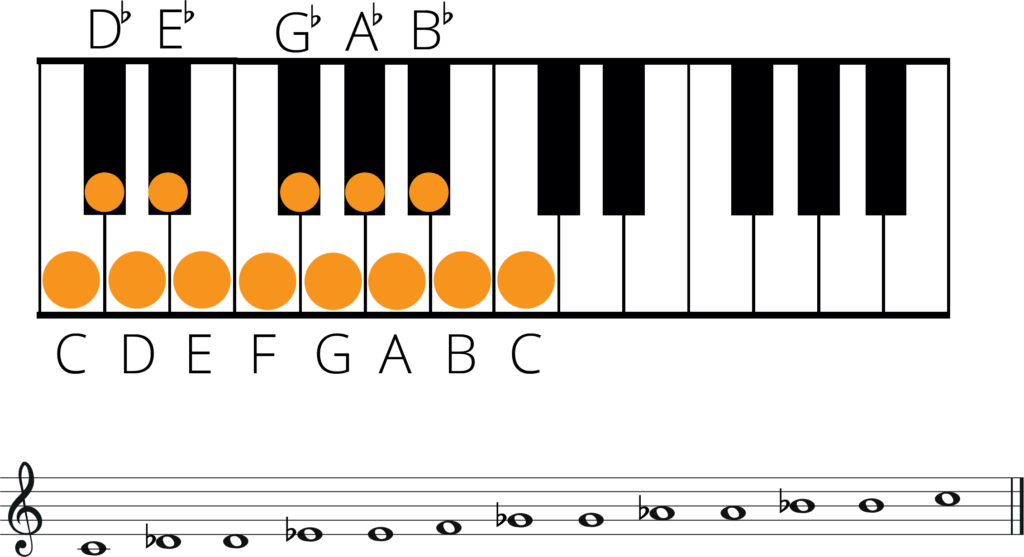
Web an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, chord or key signature that sounds the same as other note, interval, chord or key signature but is named differently. Web when a pair of notes (for example, e flat and d sharp) are sound at the same pitch, we say that they are the enharmonic equivalent of each other. Web in most cases, whether you sharp a note, or use its enharmonic equivalent will depend on the direction of movement. There are 6 common key signatures/scales that can either be written as flats or sharps. Web enharmonic notes are two notes that have the same pitch but are spelled differently.
Also, in most cases, the introduction of a chromatic note in any manner other than as a trivial passing note or auxiliary implies the introduction of a foreign mode or tonality. (this concept can also be extended to include intervals and scales.) the musical alphabet consists of seven main notes represented by seven letters: Web an enharmonic equivalent is a pitch or tone which can be spelled with two or more different letter names. Remains the same and the. These two notes share the same “pitch center,” which in music theory terms is called enharmonic equivalents.
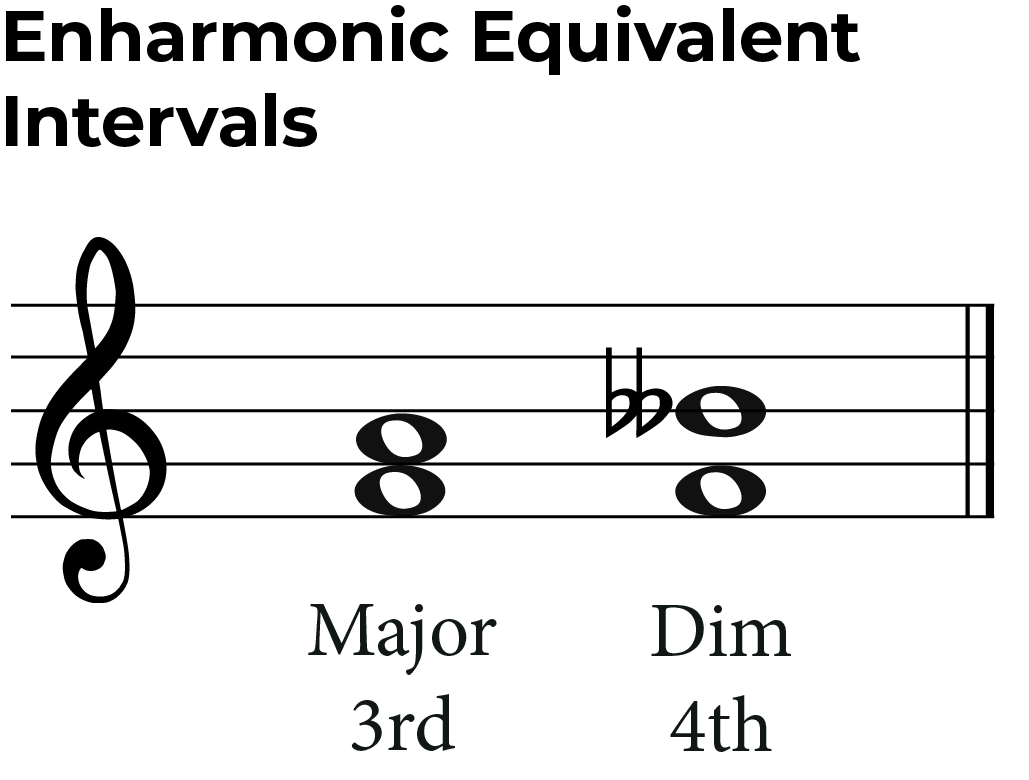
For instance if you are playing a piece of music where the key signature is sharps, then you will have notes that are referred to as being sharp, such as d sharp. Web consider the representation of enharmonic equivalents in traditional notation and on a chromatic staff, and the reasons for differentiating between them. For example, a c# is also a db. Enharmonic equivalents can come in the form of notes, keys or chords. For example, if i play a scale of c sharp major and d flat major i am playing the same note pitches. For example, c# major and db major are enharmonic equivalent keys as the underlying pitches are the same, but c# major uses sharps, and db major uses flats. These notes are usually played on different instruments or have different names. Web here is a summary chart of the common enharmonic intervals: When a note has a different name while representing a same pitch, it is known as an enharmonic equivalent note. Web how can two notes sound the same but have different names? There are 6 common key signatures/scales that can either be written as flats or sharps. Web an enharmonic equivalent is a pitch or tone which can be spelled with two or more different letter names. Here is a handy guide to the intervals of all twelve keys. Web the table below lists the enharmonic equivalents for the notes in the chromatic scale, some of which are more common than others. It works in the same way as scales and notes.
Have You Ever Wondered Why Some Notes On The Piano Have The Same Name?
Similarly, written intervals, chords, or key signatures are considered enharmonic if they represent identical pitches that are notated differently. Enharmonic equivalents can come in the form of notes, keys or chords. For instance if you are playing a piece of music where the key signature is sharps, then you will have notes that are referred to as being sharp, such as d sharp. Web in most cases, whether you sharp a note, or use its enharmonic equivalent will depend on the direction of movement.
Web Enharmonic Equivalents Often Come Into Play When Determining Key Signatures.
For example, if i play a scale of c sharp major and d flat major i am playing the same note pitches. For example, enharmonic keys include c# major and db major, f# major and gb major, b major. It works in the same way as scales and notes. A sharp symbol raises a pitch by one half step.
There Are 6 Key Signatures (3 Major, 3 Minor) That Have Equivalents:
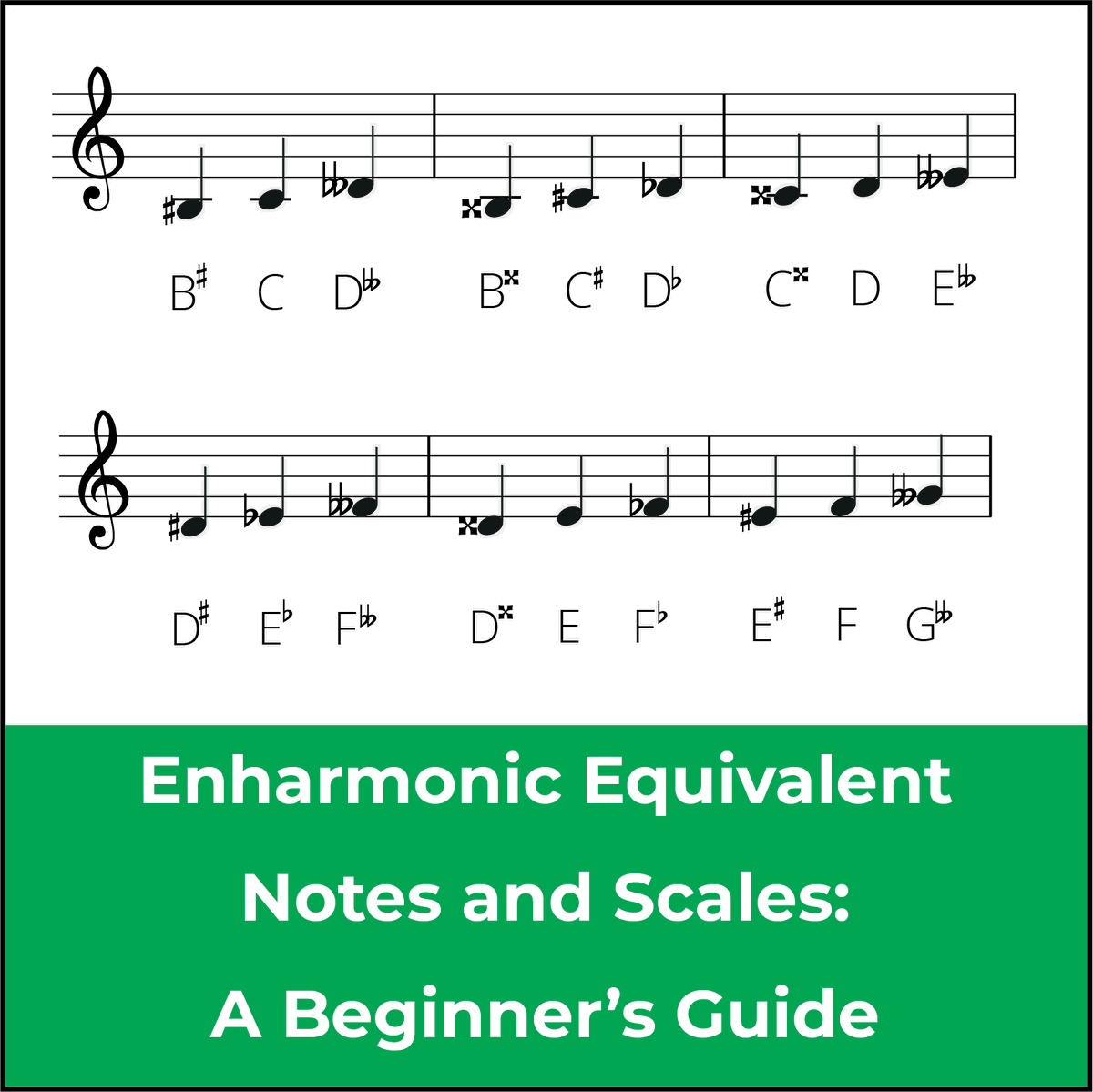
When a note has a different name while representing a same pitch, it is known as an enharmonic equivalent note. Web in music notation, sometimes a note can have two different names but have the same exact pitch. Notice that there are some enharmonic equivalents included so that each note can be written correctly. Web a good way to find enharmonic equivalents of notes or keys is to use or make a reference chart.
For Example, A C# Is Also A Db.
These are enharmonic equivalents of the notes f and c, respectively. Web when a pair of notes (for example, e flat and d sharp) are sound at the same pitch, we say that they are the enharmonic equivalent of each other. Web in music, two written notes have enharmonic equivalence if they produce the same pitch but are notated differently. These notes are usually played on different instruments or have different names.