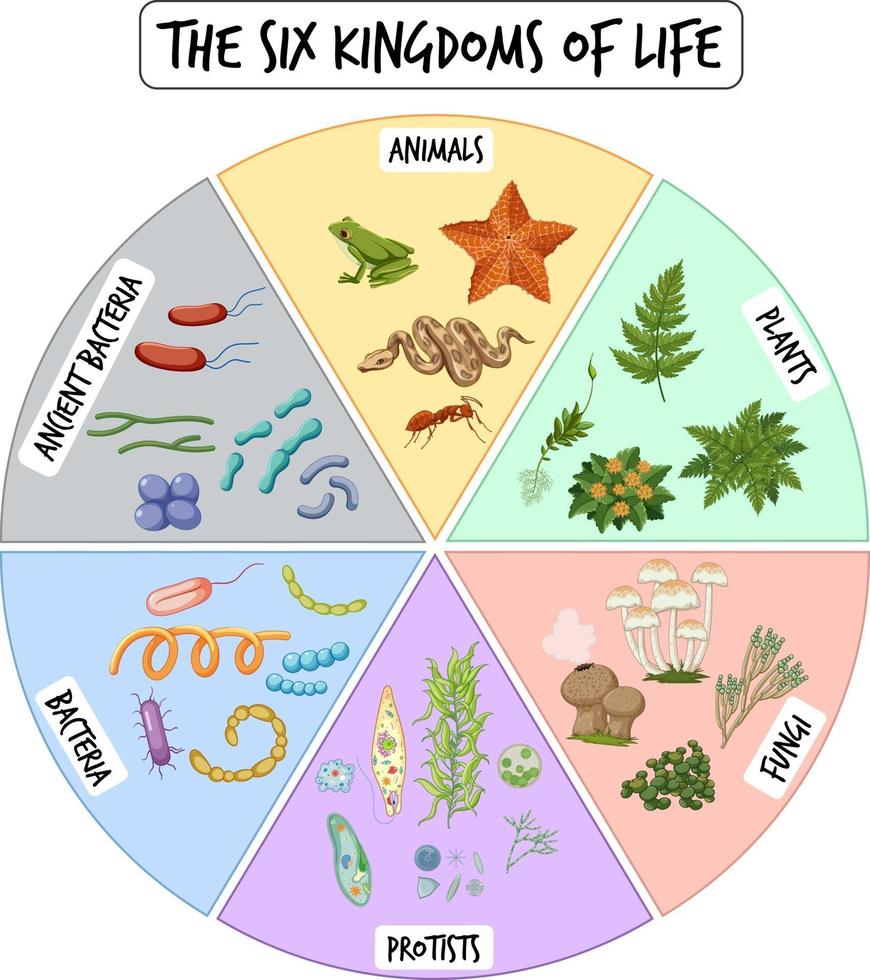
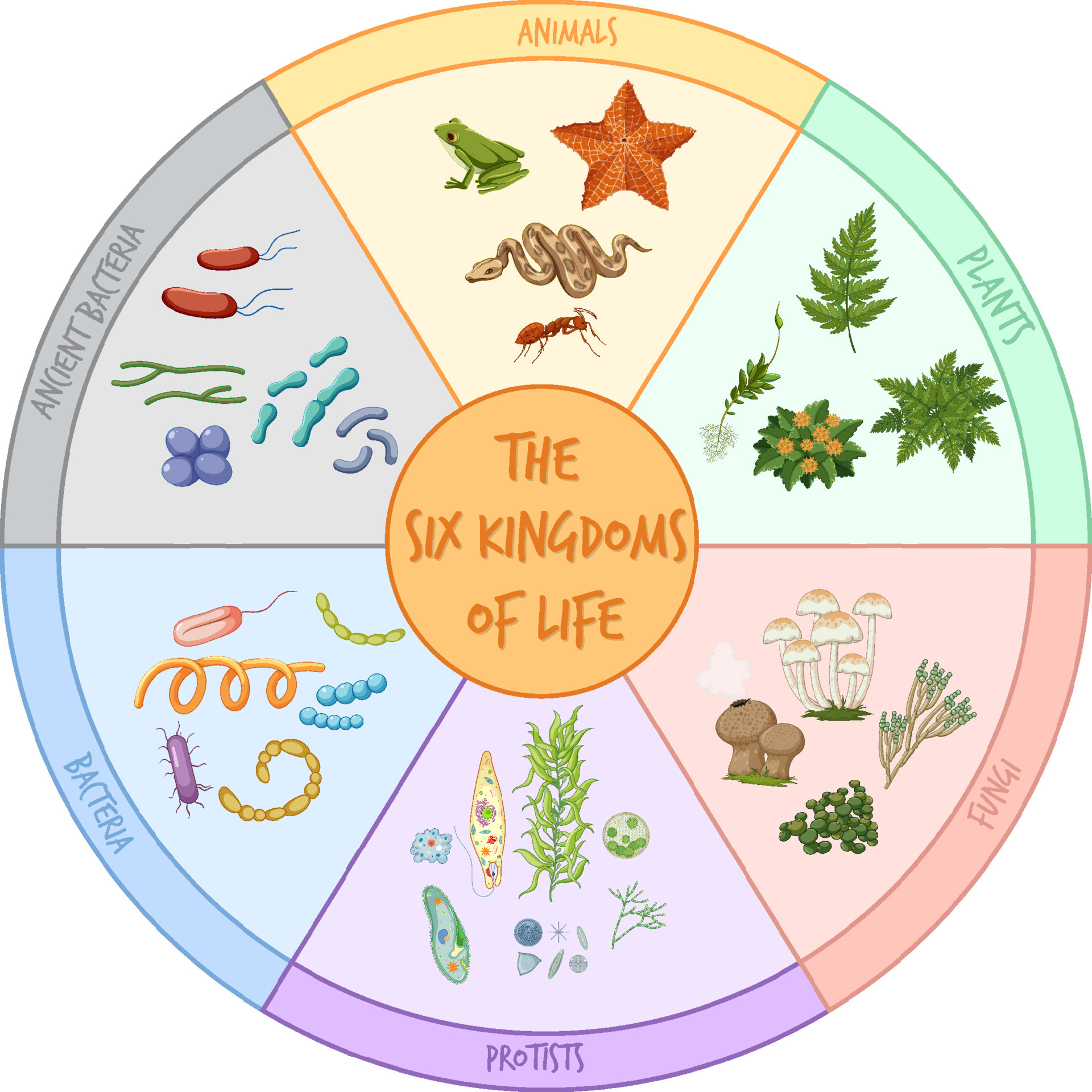
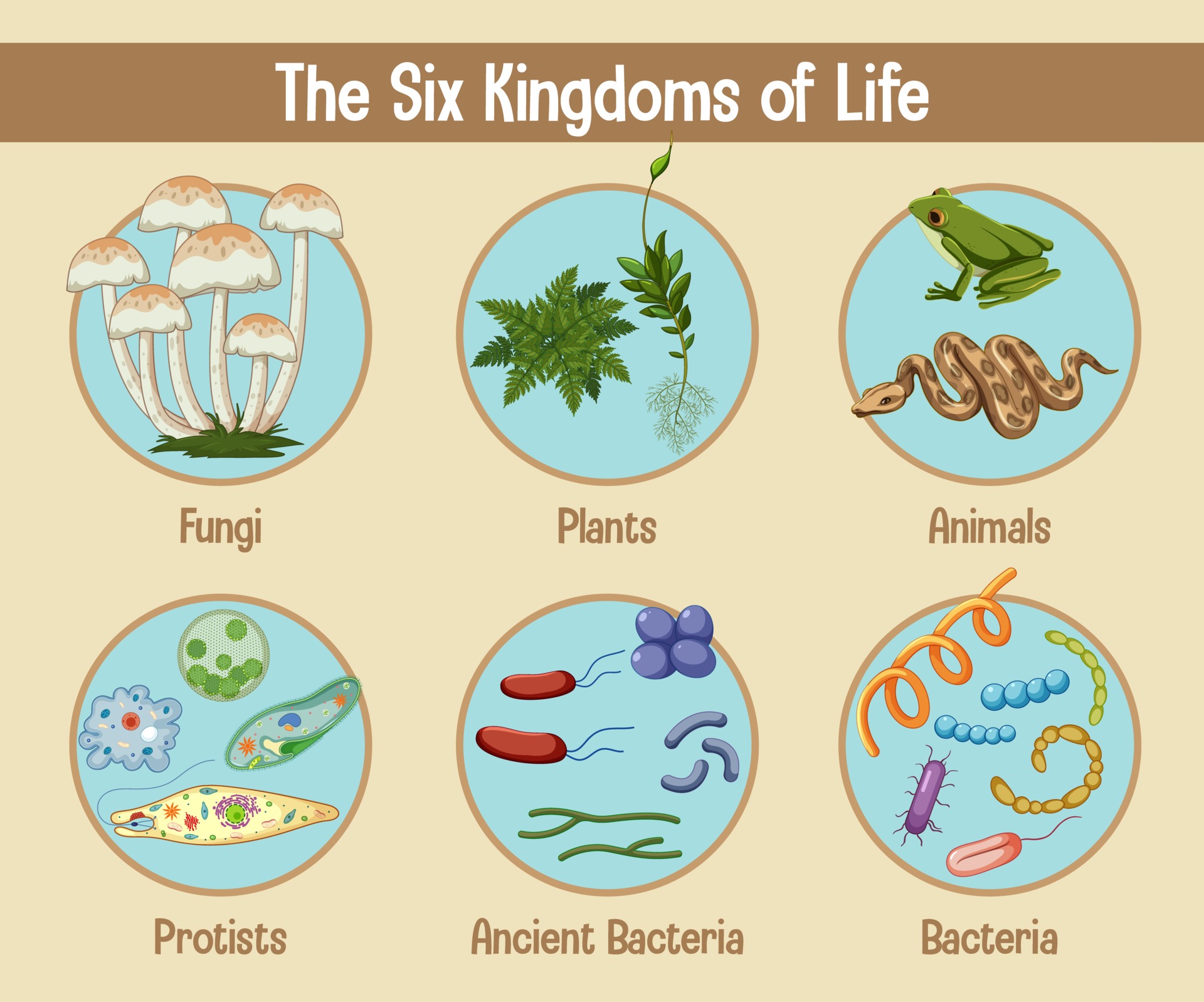
Web 6 kingdoms of life chart kingdom cell type body form cell structure nutrition habitat distinguishing characteristics examples animalia plantae fungi protista eubacteria archaebacteria. Animal, plant, fungi, protist and monera. Here is how the six kingdoms are organized. Classification attempts to impose a hierarchy on the complex and dynamic variety of life on earth by describing how different species group together and how they are related to one. Web 6 kingdoms of life, complete your thinking map by putting the title of the kingdom and some illustrated examples of organisms that belong to that kingdom in each box.
Animalia , contains general animals and is the largest kingdom with over 1 000 000 species. Web 6 kingdoms of life chart kingdom cell type body form cell structure nutrition habitat distinguishing characteristics examples animalia plantae fungi protista eubacteria archaebacteria. Web the 5 kingdoms of life are animalia, plantae, fungi, protista, and monera. 6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: Web three kingdoms of life.
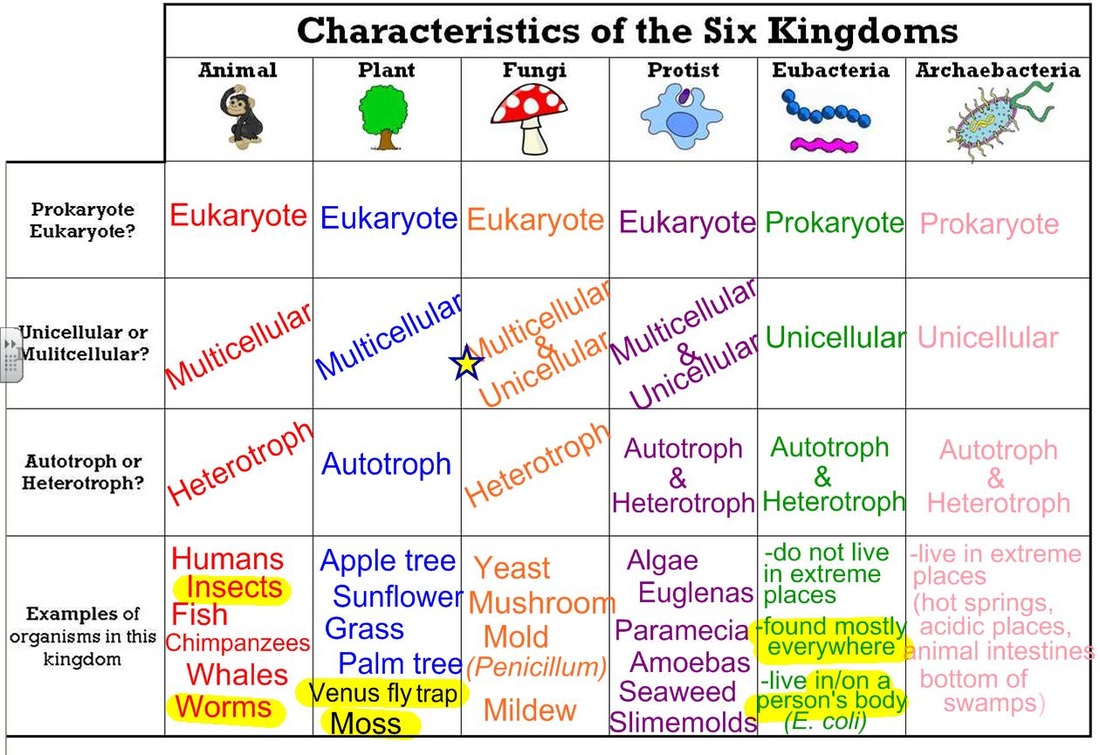
Web three kingdoms of life. Scientist group organisms into kingdoms based on these three factors: Web typically however, life is separated into six kingdoms: Collection of 5 charts includes six kingdoms of life; Bacteria, archaea, protista, plantae, fungi and animalia.
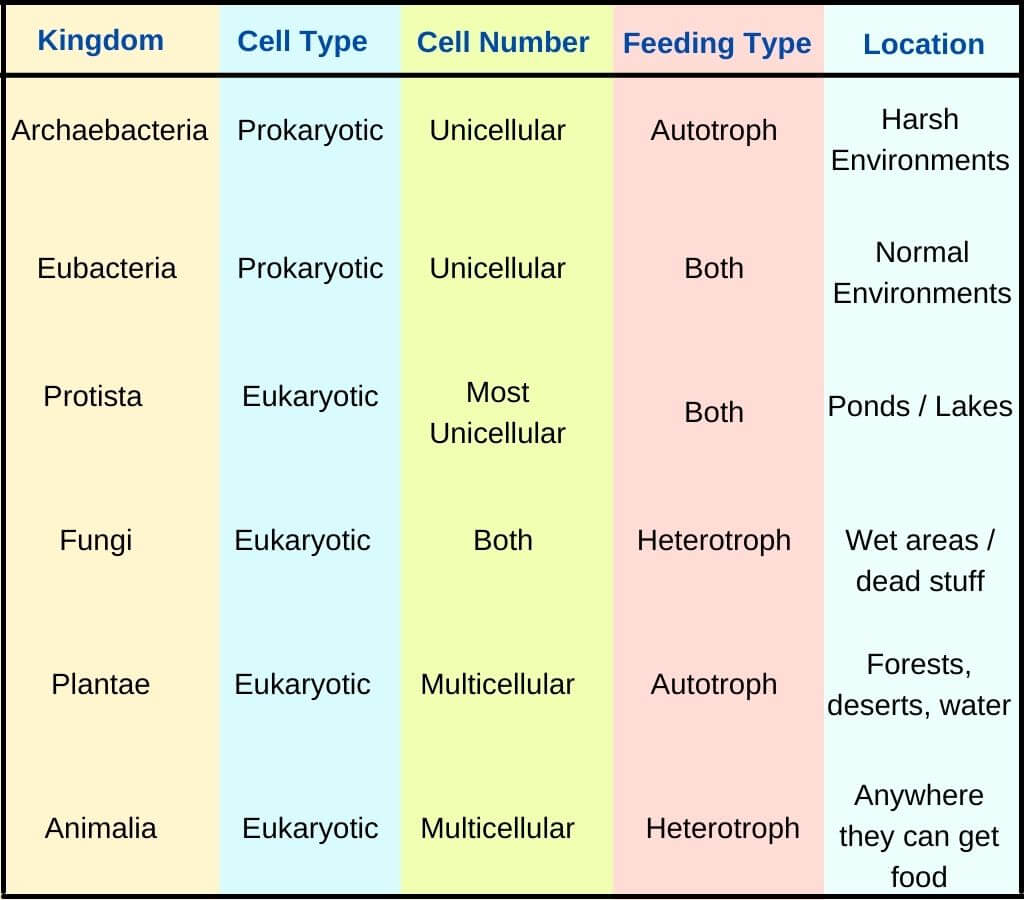
Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms: Each kingdom includes a set of organisms that share similar characteristics. Living things all have these characteristics: The most recognizable are animalia and plantae, and the four remaining are fungi, protista, archaebacteria and eubacteria. Recommended for grades 3 to 5. They adapt to their environment. Web living things are divided into five kingdoms: Each chart shows the following characteristics: When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria. Collection of 5 charts includes six kingdoms of life; Web typically however, life is separated into six kingdoms: Web there are now six commonly accepted kingdoms. We are using the montessori research and development elementary biology manual (s) as a basic guideline for this work. In biology, a kingdom of life is a taxonomy rank that is below domain and above phylum. See details for further information (below)
Web 6 Kingdoms Of Life, Complete Your Thinking Map By Putting The Title Of The Kingdom And Some Illustrated Examples Of Organisms That Belong To That Kingdom In Each Box.
Web under the three domains are six kingdoms in taxonomy: The chart below shows how the kingdoms have changed over time. Web living things are divided into five kingdoms: Archaebacteria, eubacteria, fungi, protista, plants and animals.
Here Is How The Six Kingdoms Are Organized.
Two separate charts that display the characteristics for the 6 kingdoms of life. Nobody knows for certain when, how or why life began on earth, but aristotle observed 2,400 years ago that all the planet's biodiversity was of animal or plant origin. Web what are the six kingdoms of life? When there are 6 kingdoms, monera breaks into eubacteria and archaebacteria.
This Isn't As Easy As It Seemed At First!
6 kingdoms of life, from simplest to most complex, are as follows: Living things all have these characteristics: Web every living creature on earth belongs to a kingdom. Scientists debate how many kingdoms there are, with many arguing that there are six.
Recommended For Grades 3 To 5.
Web today all living organisms are classified into one of six kingdoms: The organisms in each kingdom are considered biologically distinct from the others. They require, take in, and use energy. Web the six kingdoms are eubacteria, archae, protista, fungi, plantae, and animalia.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/six-kingdoms-of-life-373414-Final1-5c538e2446e0fb00013faa3c.png)