Burns + inhalation injury or need to ventilate. Superficial burns (erythema only) are not included in estimating burn tbsa. Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue as a result of exposure to heat (eg, hot liquids [scalds], hot solids [contact burns], smoke [inhalation injury], or direct flames), ultraviolet/infrared radiation, radioactive materials, electricity, friction, chemicals, or. The majority of admissions result from scalds, followed by contact and flame burns. Web approximately 6,600 (17.5% of all trauma cases) are admitted for burns management.
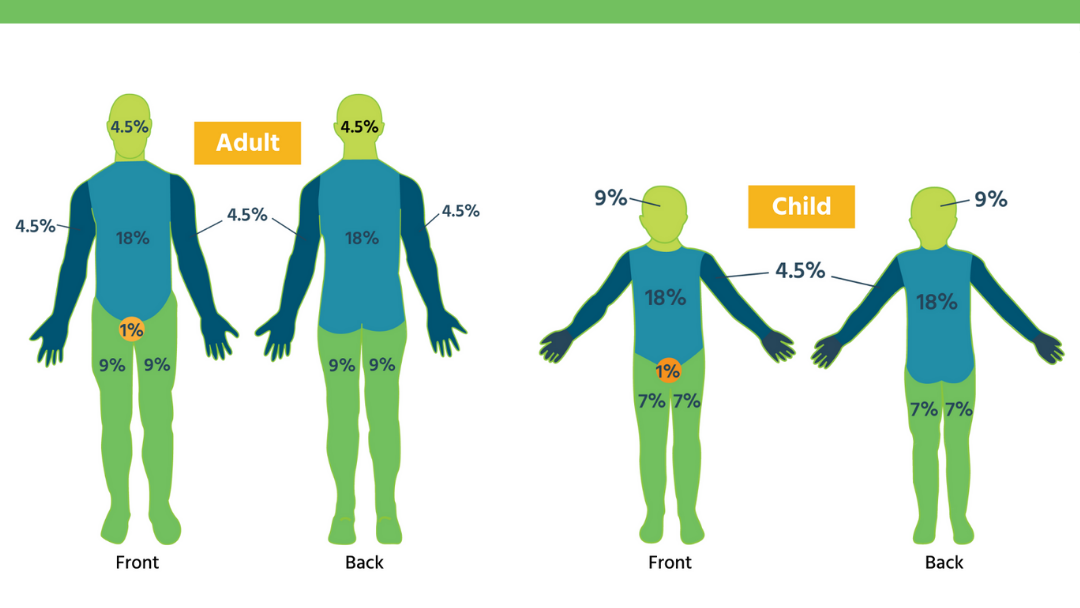
*areas of difference between the pediatric and adult population are represented by bold italics. Web •to appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient •to provide appropriate burn care management for inpatients, including fluid resuscitation, dressing changes, and pain management Overestimation occurs when simple erythema is included. Web examine whether chest wall has been effective by burn as may develop respiratory failure from exhaustion and extreme pain; The incidence of burns is higher in children than in adults.
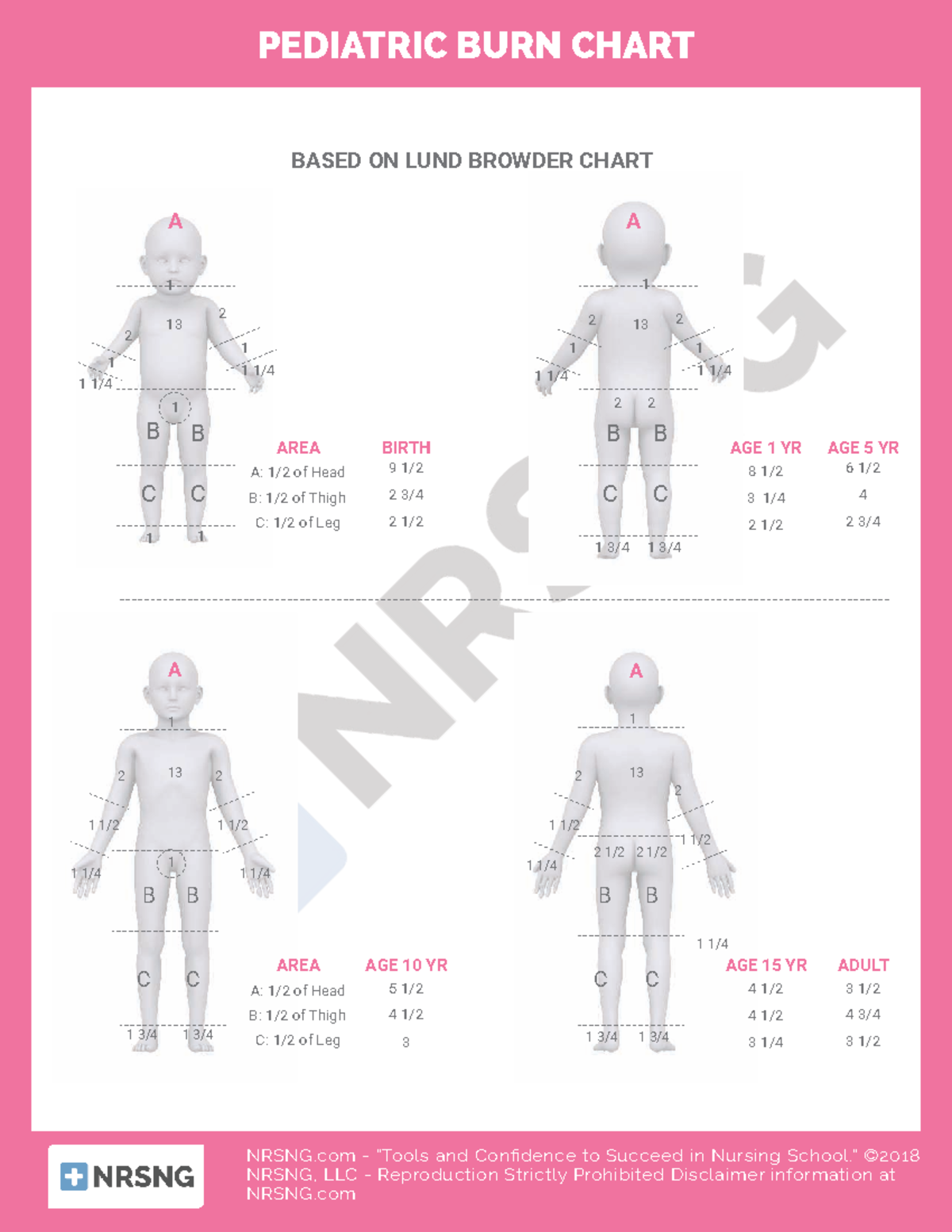
Less common injuries in children include electrical, chemical and radiation burns. Newton browder, based on their experiences in treating over 300 burn victims injured at the cocoanut grove fire in boston in 1942. Web paediatric lund and browder chart. Burns + inhalation injury or need to ventilate. Superficial burns (erythema only) are not included in estimating burn tbsa.
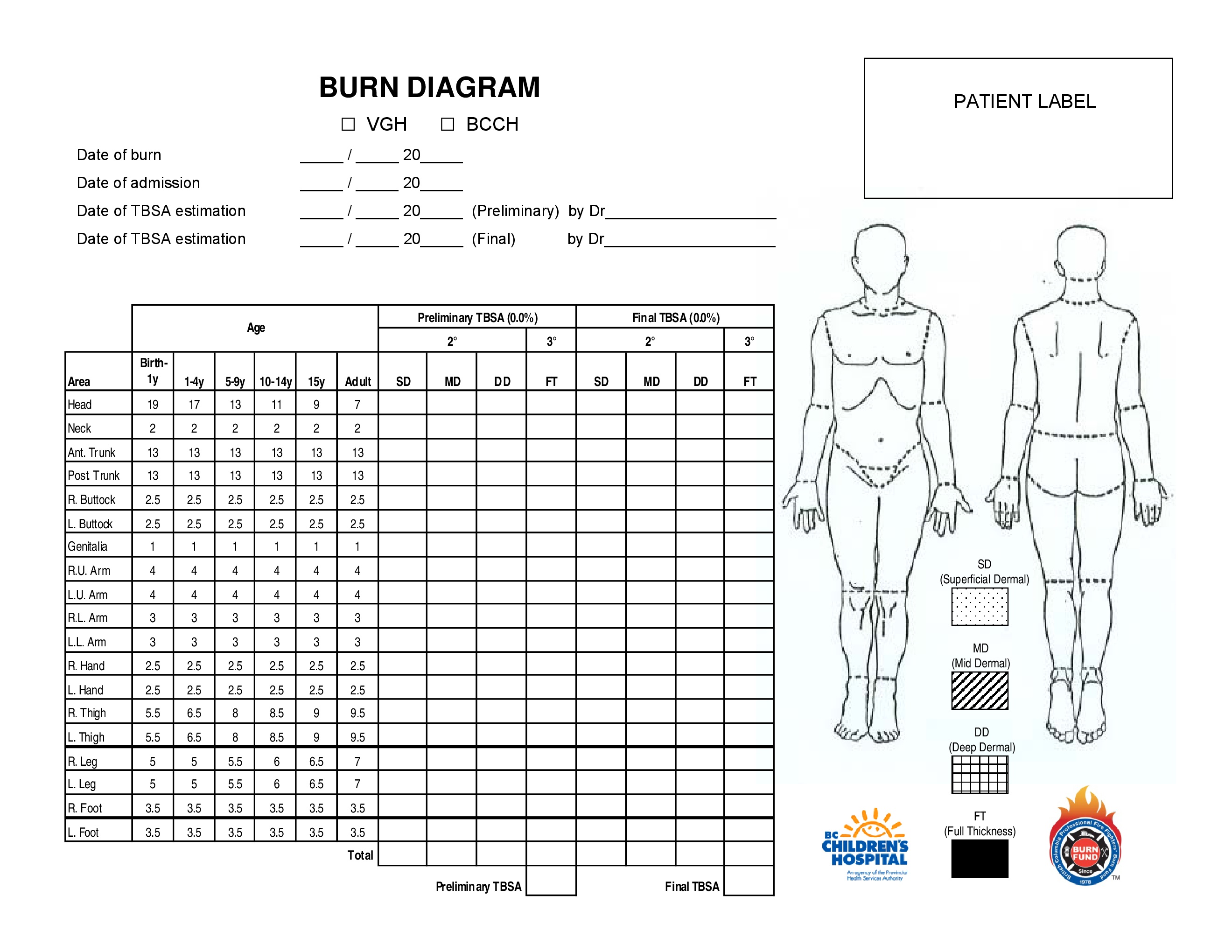
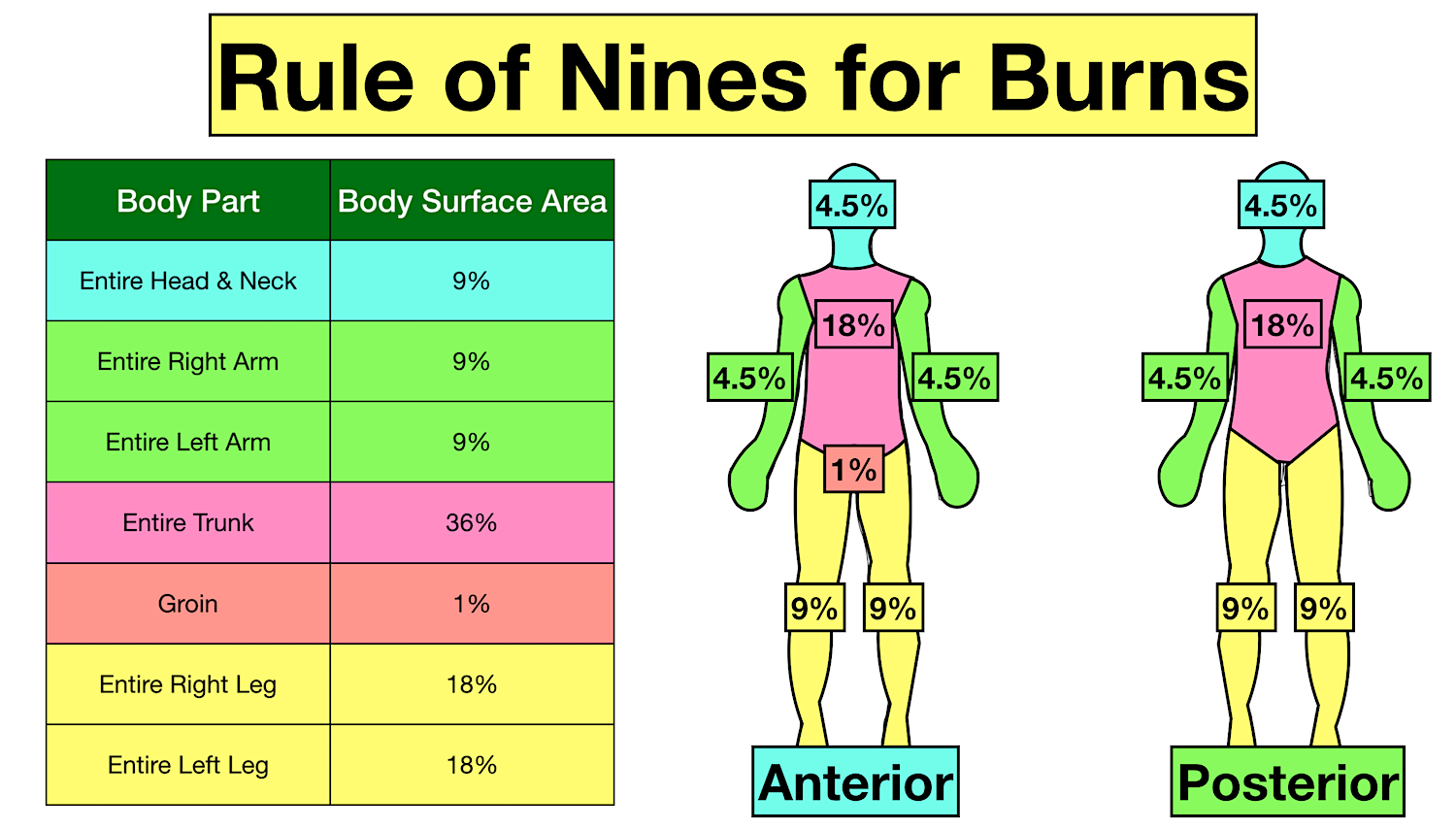
Web this topic will review the emergency management of moderate to severe thermal burns in children ( table 1 ). Less common injuries in children include electrical, chemical and radiation burns. Web burn injuries healing prior to 3 weeks also have the potential to develop hypertrophic scarring, even when prescribed prophylactic conservative scar interventions. The incidence of burns is higher in children than in adults. The majority of admissions result from scalds, followed by contact and flame burns. Calculate requirements from time of. This practice guideline will outline the essential elements of. Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue as a result of exposure to heat (eg, hot liquids [scalds], hot solids [contact burns], smoke [inhalation injury], or direct flames), ultraviolet/infrared radiation, radioactive materials, electricity, friction, chemicals, or. The palm (including fingers), of the patient, equates to approximately 1% of the patient’s body surface. Web the paediatric lund and browder chart (modified rule of nines chart) should be used to enable accurate calculations. Paediatric burn and scald management in a low resource setting: (see treatment of minor thermal burns.) Newton browder, based on their experiences in treating over 300 burn victims injured at the cocoanut grove fire in boston in 1942. *infants and the elderly have thinner skin; Web the goal is management of burns shock, through optimal replacement of fluid losses to maximise wound and body perfusion, and minimise wound and body oedema and associated adverse effects.
Web Pediatric Burns Are Injuries To The Skin Or Other Tissue As A Result Of Exposure To Heat (Eg, Hot Liquids [Scalds], Hot Solids [Contact Burns], Smoke [Inhalation Injury], Or Direct Flames), Ultraviolet/Infrared Radiation, Radioactive Materials, Electricity, Friction, Chemicals, Or.
A reference guide and review. Web paediatric lund and browder chart. The american burn association (aba) has published an educational resource that reviewed the classification and management of the burn wound. An alternative rule is that the patient's palm and fingers represent 1% of the body surface.
*Areas Of Difference Between The Pediatric And Adult Population Are Represented By Bold Italics.
Web this topic will review the emergency management of moderate to severe thermal burns in children ( table 1 ). The majority of admissions result from scalds, followed by contact and flame burns. Burn injuries are common in children. Overestimation occurs when simple erythema is included.
Web Although Most Burns In Children Are Small And Can Be Managed With Care Provided In The Outpatient Setting, There Is A Significant Number Of Children With More Serious.
Guidelines on the management of children with burns. Circulation + control of external haemorrhage. Web •to appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient •to provide appropriate burn care management for inpatients, including fluid resuscitation, dressing changes, and pain management Web the total body surface area (tbsa) of a burn was traditionally assessed using lund and browder burns chart that denotes the percentage of body surface and changes with age of the child (fig 2).
Superficial Burns (Erythema Only) Are Not Included In Estimating Burn Tbsa.
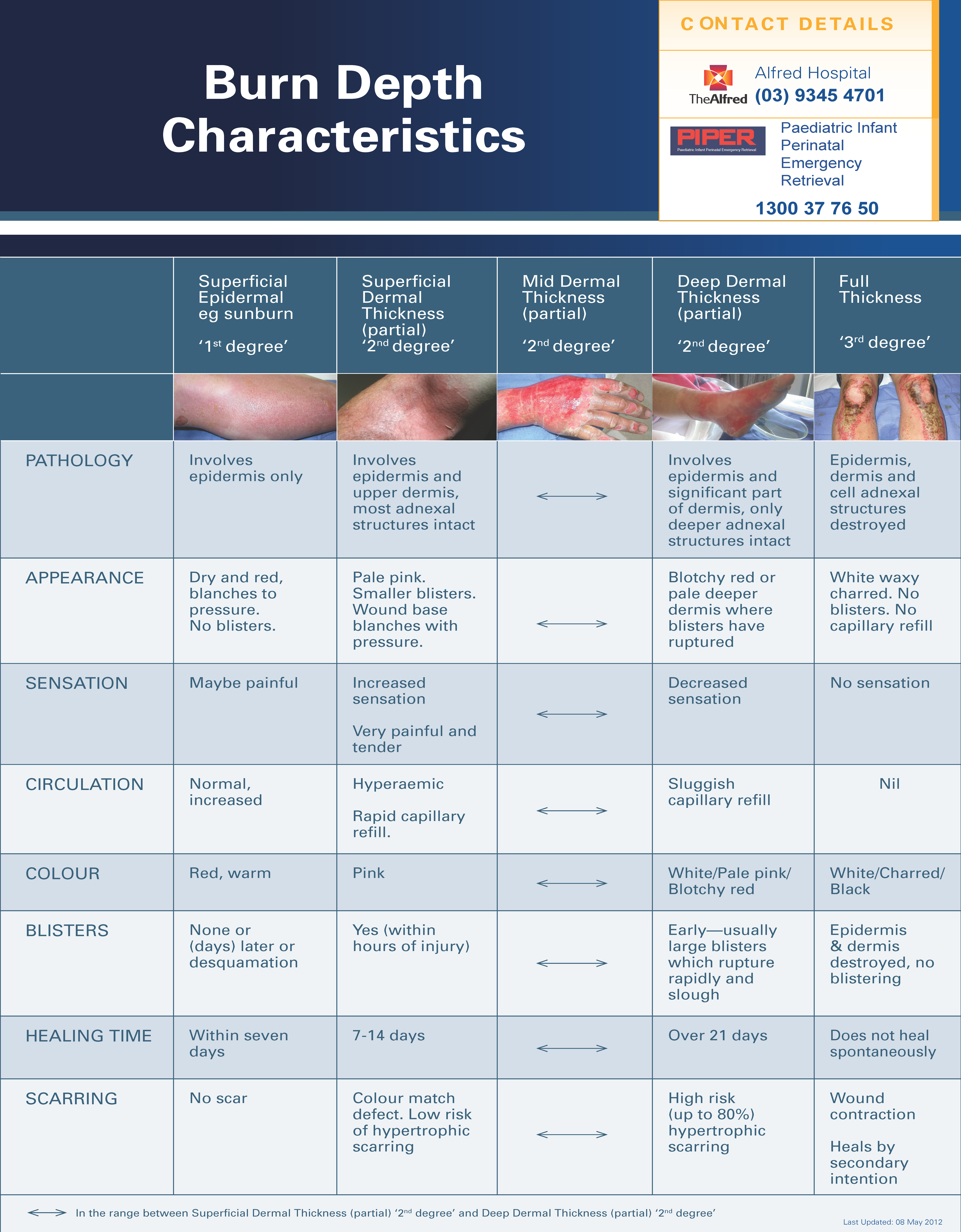
*infants and the elderly have thinner skin; Web appropriate burn wound care may necessitate multiple treatment modalities for different parts of a burn wound depending on the burn depth of each injured part. Consequently, burns may be deeper and more severe than they initially appear (american burn association, 2018). Charles lund, senior surgeon at boston city hospital, and dr.