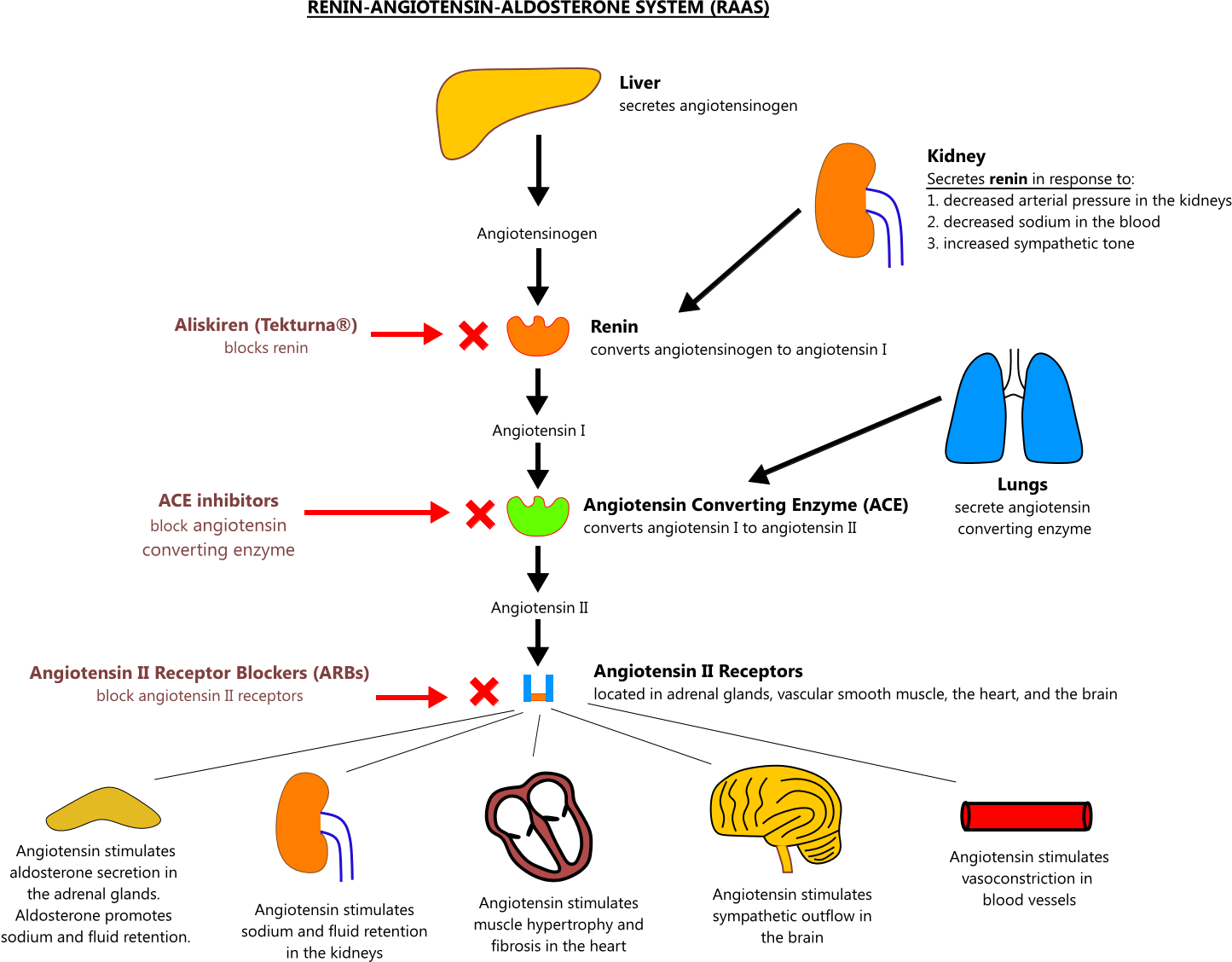
Gram project is a medical education resource website containing diagrams, tables and flowcharts for all your quick referencing, revision and teaching needs. This article will describe the system, discuss how the system is regulated, and outline some clinically relevant points around it. 1) renin, 2) angiotensin, and 3) aldosterone. Web an overview of the physiological mechanisms which regulate blood pressure (bp) including the baroreceptor reflex, raas, adh and anp. Web flowchart showing the clinical effects of raas activity and the sites of action of ace inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers.
Gram project is a medical education resource website containing diagrams, tables and flowcharts for all your quick referencing, revision and teaching needs. When blood pressure falls (for systolic, to 100 mm hg or lower), the kidneys release the enzyme renin into the bloodstream. Dysregulated raas is implicated in high blood. Raas signaling enhances cell proliferation in malignancy directly and indirectly by affecting tumor cells and modulating angiogenesis. Web flowchart showing the clinical effects of raas activity and the sites of action of ace inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers.
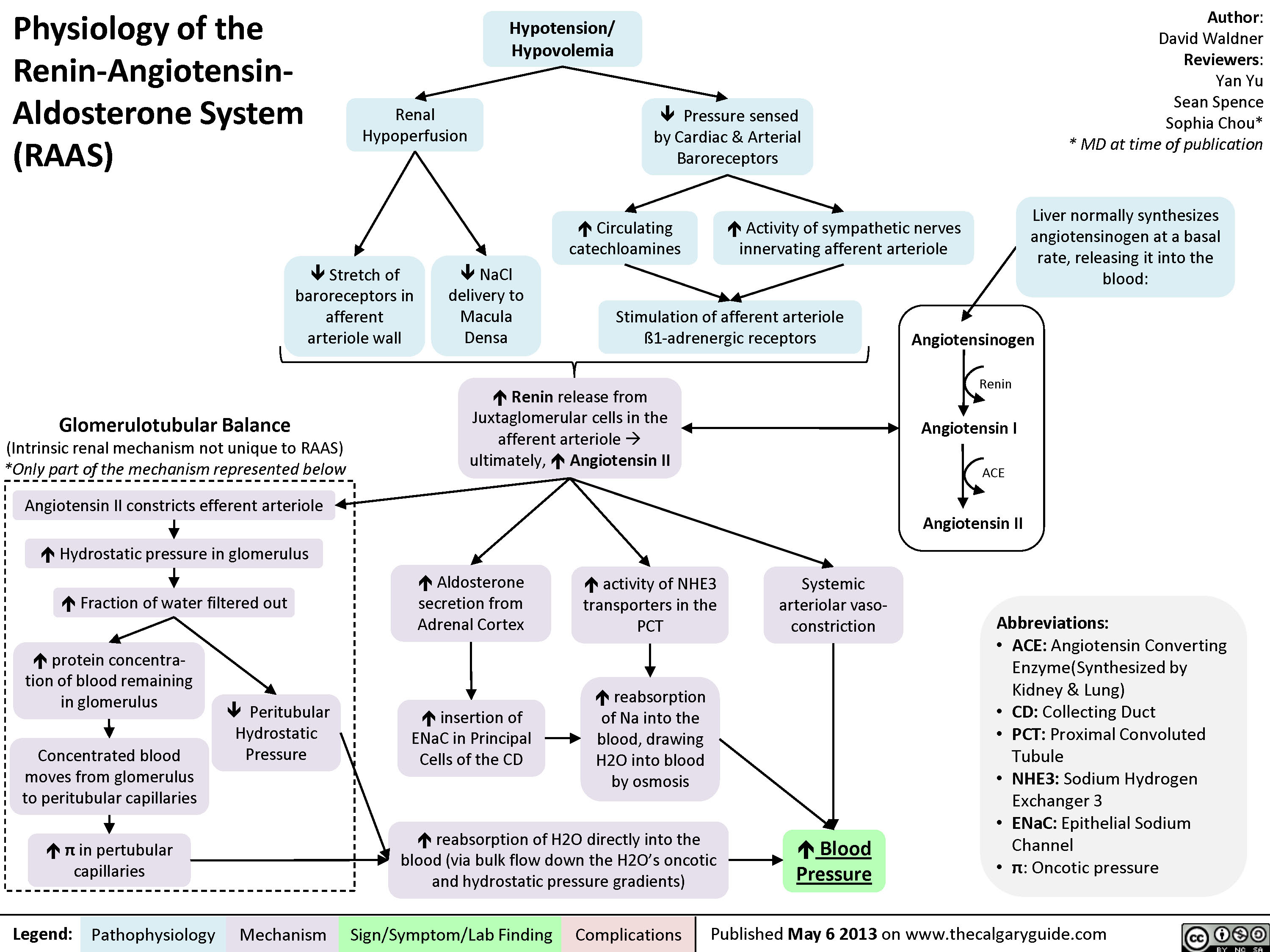
Dysregulated raas is implicated in high blood. This article will describe the system, discuss how the system is regulated, and outline some clinically relevant points around it. When your blood pressure falls, your kidneys release the enzyme renin into your bloodstream. Web the primary stimulus for increased renin secretion is decreased blood flow to the kidneys, which may be caused by loss of sodium and water (as a result of diarrhea, persistent vomiting, or excessive perspiration) or by narrowing of a renal artery. Raas signaling enhances cell proliferation in malignancy directly and indirectly by affecting tumor cells and modulating angiogenesis.
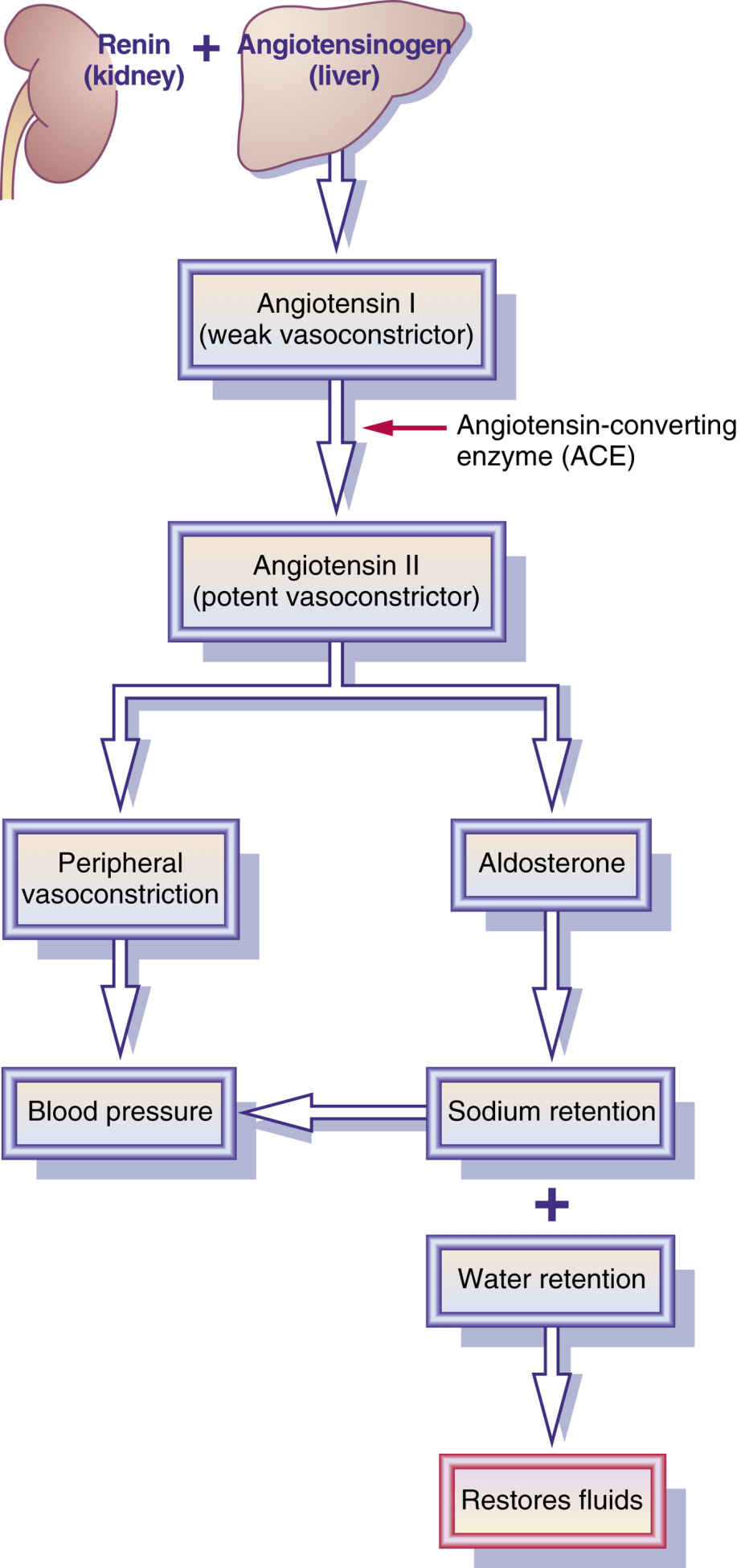
While the baroreceptor reflex responds short term to decreased arterial pressure, the raas is responsible for acute and chronic alterations. Gram project is a medical education resource website containing diagrams, tables and flowcharts for all your quick referencing, revision and teaching needs. Furthermore, the raas has various effects on multiple organs via paracrine processes. Web the primary stimulus for increased renin secretion is decreased blood flow to the kidneys, which may be caused by loss of sodium and water (as a result of diarrhea, persistent vomiting, or excessive perspiration) or by narrowing of a renal artery. Web an overview of the physiological mechanisms which regulate blood pressure (bp) including the baroreceptor reflex, raas, adh and anp. Activation of the raas system occurs after renin release in the kidneys that catalyzes the synthesis. Renin splits angiotensinogen, a large protein that circulates in the bloodstream, into pieces. Dysregulated raas is implicated in high blood. When your blood pressure falls, your kidneys release the enzyme renin into your bloodstream. Renin splits angiotensinogen, a protein your liver makes and releases, into pieces. One piece is the hormone angiotensin i. Web the system is mainly comprised of the three hormones renin, angiotensin ii, and aldosterone. A decrease in arterial blood pressure is sensed by the kidneys as decreased renal perfusion pressure. An overview of the normal function of the system, as well as ramifications of its dysfunction. Primarily it is regulated by the rate of renal blood flow.
Activation Of The Raas System Occurs After Renin Release In The Kidneys That Catalyzes The Synthesis.
Renin splits angiotensinogen, a protein your liver makes and releases, into pieces. An overview of the normal function of the system, as well as ramifications of its dysfunction. Web the primary stimulus for increased renin secretion is decreased blood flow to the kidneys, which may be caused by loss of sodium and water (as a result of diarrhea, persistent vomiting, or excessive perspiration) or by narrowing of a renal artery. The liver, lung, adrenal gland, kidney, and vasculature are all prominently involved.
While The Baroreceptor Reflex Responds Short Term To Decreased Arterial Pressure, The Raas Is Responsible For Acute And Chronic Alterations.
Primarily it is regulated by the rate of renal blood flow. One piece is the hormone angiotensin i. As the name implies, there are three important components to this system: Dysregulated raas is implicated in high blood.
This Article Will Describe The System, Discuss How The System Is Regulated, And Outline Some Clinically Relevant Points Around It.
Learn how juxtaglomerular cells in the kidneys release renin in response to low blood pressure, triggering a cascade of hormones that ultimately raise blood pressure. Renin splits angiotensinogen, a large protein that circulates in the bloodstream, into pieces. Gram project is a medical education resource website containing diagrams, tables and flowcharts for all your quick referencing, revision and teaching needs. Web the system is mainly comprised of the three hormones renin, angiotensin ii, and aldosterone.
When Blood Pressure Falls (For Systolic, To 100 Mm Hg Or Lower), The Kidneys Release The Enzyme Renin Into The Bloodstream.
Raas signaling enhances cell proliferation in malignancy directly and indirectly by affecting tumor cells and modulating angiogenesis. It never hurts to review basic physiologic principles, right? 1) renin, 2) angiotensin, and 3) aldosterone. Furthermore, the raas has various effects on multiple organs via paracrine processes.



![The ReninAngiotensinAldosterone [RAAS] Pathway EXPLAINED YouTube](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/_S59qSuosgE/maxresdefault.jpg)

