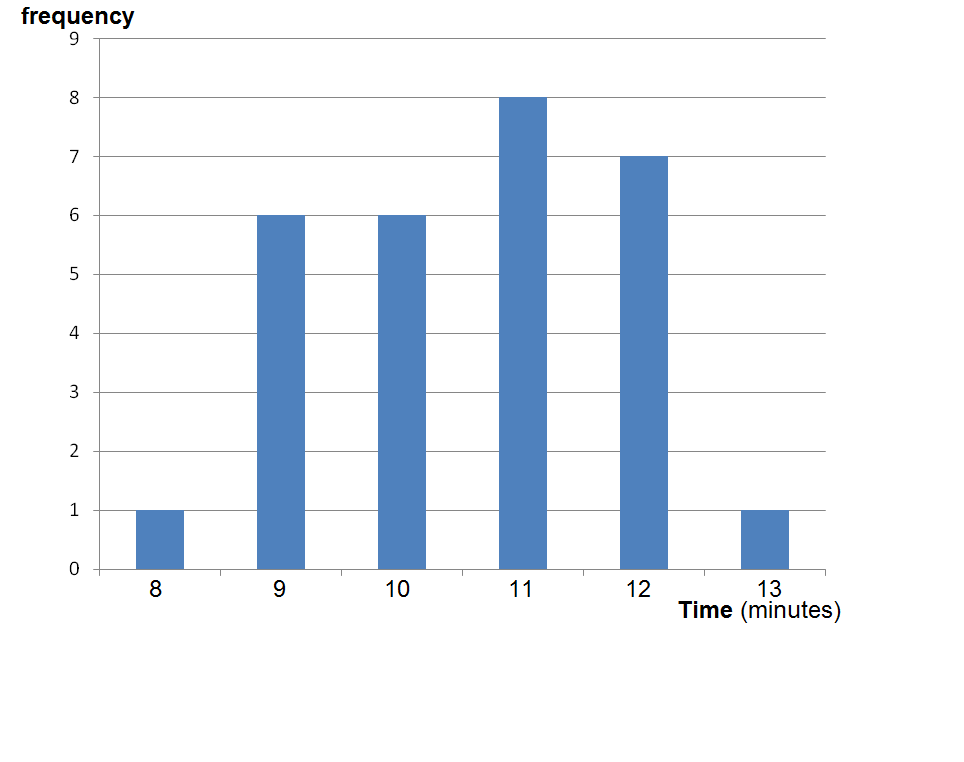
One bar is plotted for each level of the categorical variable, each. Web how to make a relative frequency bar graph. Web a bar with a height equal to the frequency (or relative frequency) is built above each observed value or class. Your team has won 9 games from a total of 12 games played: In other words, it tells.
In a histogram, classes may be identified by their. To construct a bar graph, we need to. Then go to the charts group in the insert tab and click the first chart type in insert column or bar chart: Generates editable bar charts that represent categorical variables (e.g.,. For example, numbers of people in different ethnic groups, or number of.
Upload your data set using the input at the top of the page. Relative frequencies show how often something happens compared to the total number. These displays show all possible values of the variable along. Web how often something happens divided by all outcomes. Below are a frequency table, a pie chart, and a bar graph for.
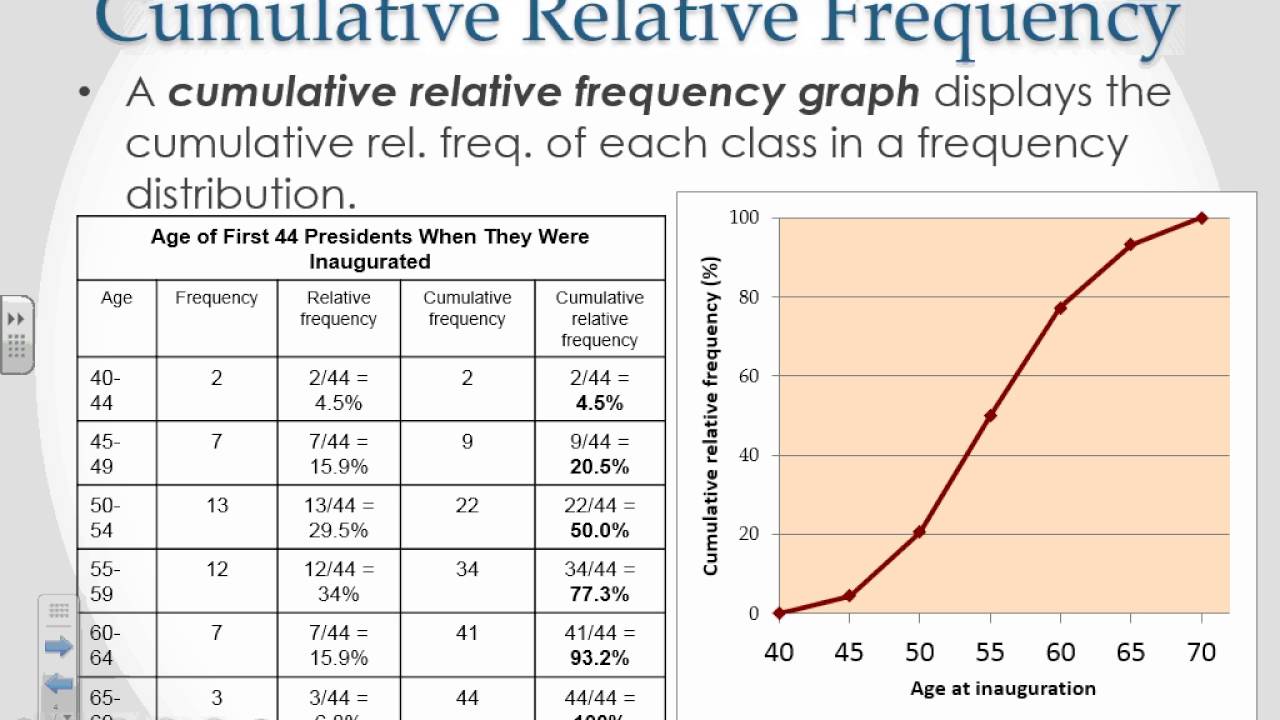
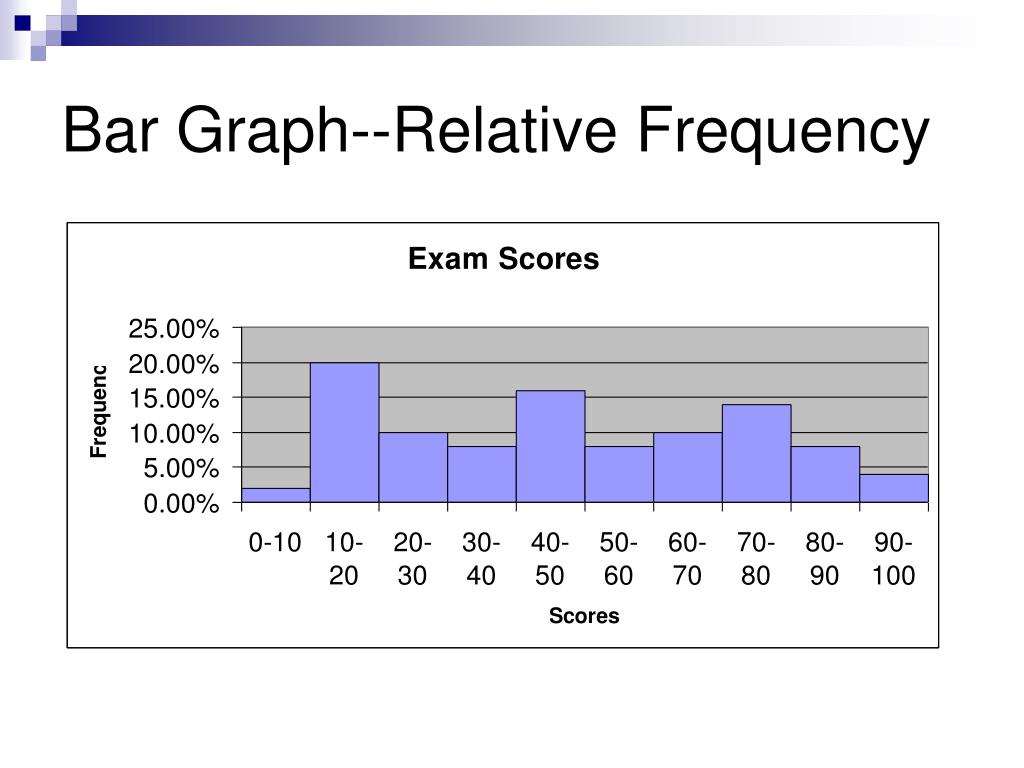
Web download all guides. For example, numbers of people in different ethnic groups, or number of. Select the column, x, that you want to see frequencies for. Web a relative frequency graph is a type of bar chart that shows the relative frequencies corresponds to the values in a sample, with respect to the total number of sample data. Web frequency tables, pie charts, and bar charts can be used to display the distribution of a single categorical variable. Web how to make a frequency bar graph. These displays show all possible values of the variable along. Web explore different ways of representing, analyzing, and interpreting data, including line plots, frequency tables, cumulative and relative frequency tables, and bar graphs. Web you can also draw a bar graph using relative frequency on the vertical axis. Select a column, x, to view frequencies for. Web you can also use bar charts to display relative frequency distributions. Web a bar with a height equal to the frequency (or relative frequency) is built above each observed value or class. This is useful when you want to compare two samples with different sample sizes. One bar is plotted for each level of the categorical variable, each. Web simply highlight the relative frequencies:
Web You Can Also Draw A Bar Graph Using Relative Frequency On The Vertical Axis.
Then go to the charts group in the insert tab and click the first chart type in insert column or bar chart: Web how often something happens divided by all outcomes. Web the main objective of a standard bar chart is to compare numeric values between levels of a categorical variable. Web a bar chart is used when you want to show a distribution of data points or perform a comparison of metric values across different subgroups of your data.
To Construct A Bar Graph, We Need To.
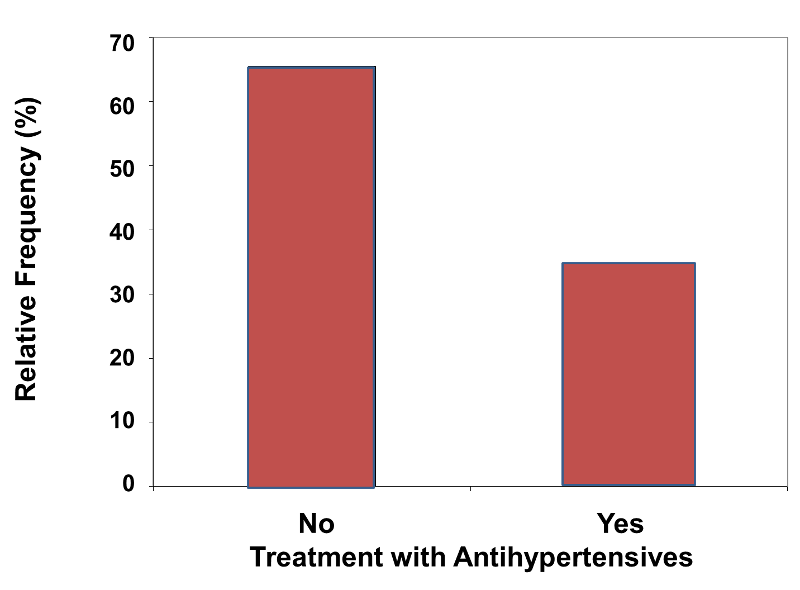
Web you can also use bar charts to display relative frequency distributions. A bar graph is a graph that displays a bar for each category with the length of each bar indicating the frequency of that category. Web this online bar graph generator will provide you will all the tools you need to make a quick and nice looking bar chart. The graph below depicts the same information as the table.
Web Bar Charts Are Used For (Relative) Frequencies In Classes Of Categorical Variables, Or For Discrete Data.
Web a bar with a height equal to the frequency (or relative frequency) is built above each observed value or class. The frequency of winning is 9. Web to visualize the relative frequency distribution, you can create a frequency distribution histogram or bar chart, depending on the type of data you are working with. Upload your dataset using the input at the top of the page.
Web Please Enter Your Category And Frequency Count Data, And Then Press The Create Bar Chart Button.
Web the relative frequency definition is the number of times an event occurs during experiments divided by the number of total trials conducted. Web a relative frequency graph is a type of bar chart that shows the relative frequencies corresponds to the values in a sample, with respect to the total number of sample data. Relative frequencies show how often something happens compared to the total number. Below are a frequency table, a pie chart, and a bar graph for.




![[最新] quantitative vs categorical graphs 324612Quantitative and](https://calcworkshop.com/wp-content/uploads/frequency-bar-graph.png)