The process takes place in the cytoplasm of a cell and does not require oxygen. 4.5/5 (12k reviews) Glucose + 2nad+ + 2 pi + 2 adp = 2 pyruvate + 2 atp + 2 nadh + 2 h2o. C6h12o6 + 2adp + 2pi + 2nad+ → 2c3h4o3 + 2h2o + 2atp + 2nadh + 2h+ c6h12o6 is glucose and c3h4o3 is pyruvate. It produces two molecules of pyruvate, atp, nadh and water.
Web glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. You’ll see that by making connections you’ll understand glycolysis much better. Explain how cells cope with the lack of oxygen and inability of pyruvate (end product of glycolysis) to enter the tca cycle and how the process of anaerobic glycolysis continues. What starts glycolysis in cells? 4.5/5 (12k reviews)
Web let's explore the process of glycolysis, the first phase of cellular respiration. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? Web learn about what is glycolysis, where does it occur, its steps or pathway, and purpose, along with diagram. What happens to pyruvate after glycolysis? Glucose enters heterotrophic cells in two ways.
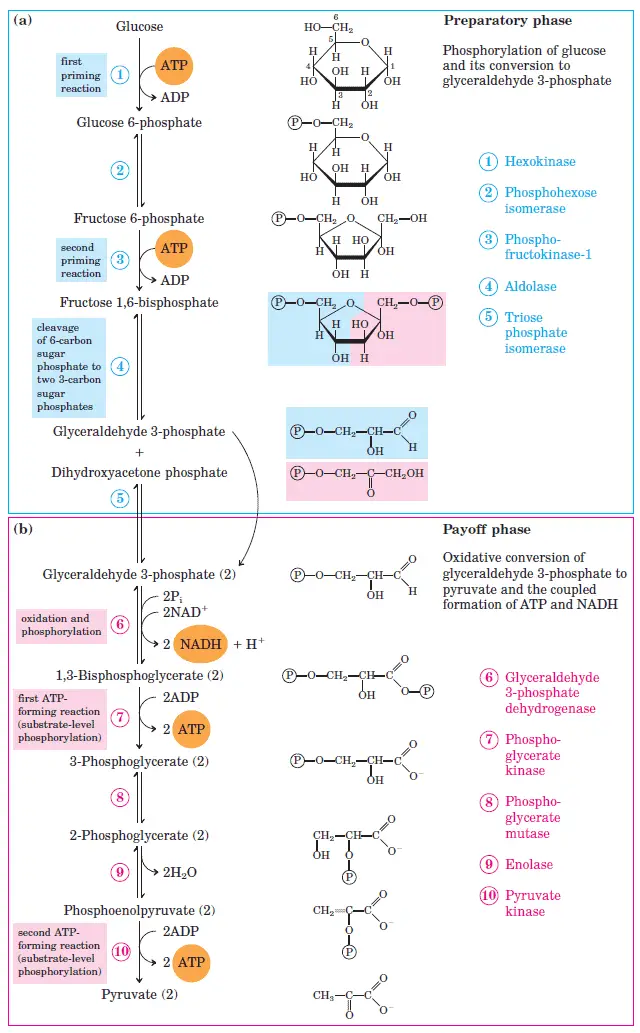
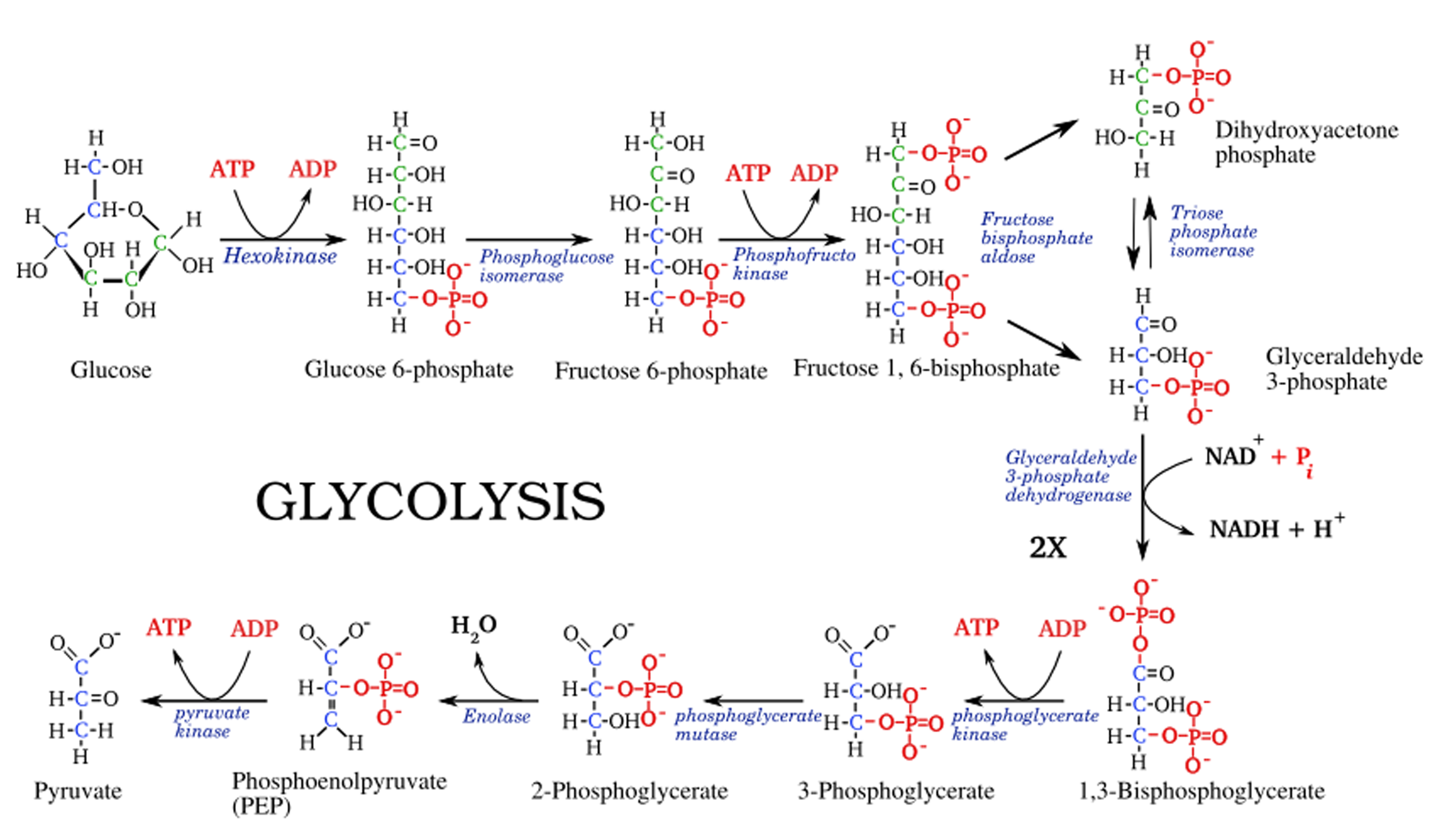
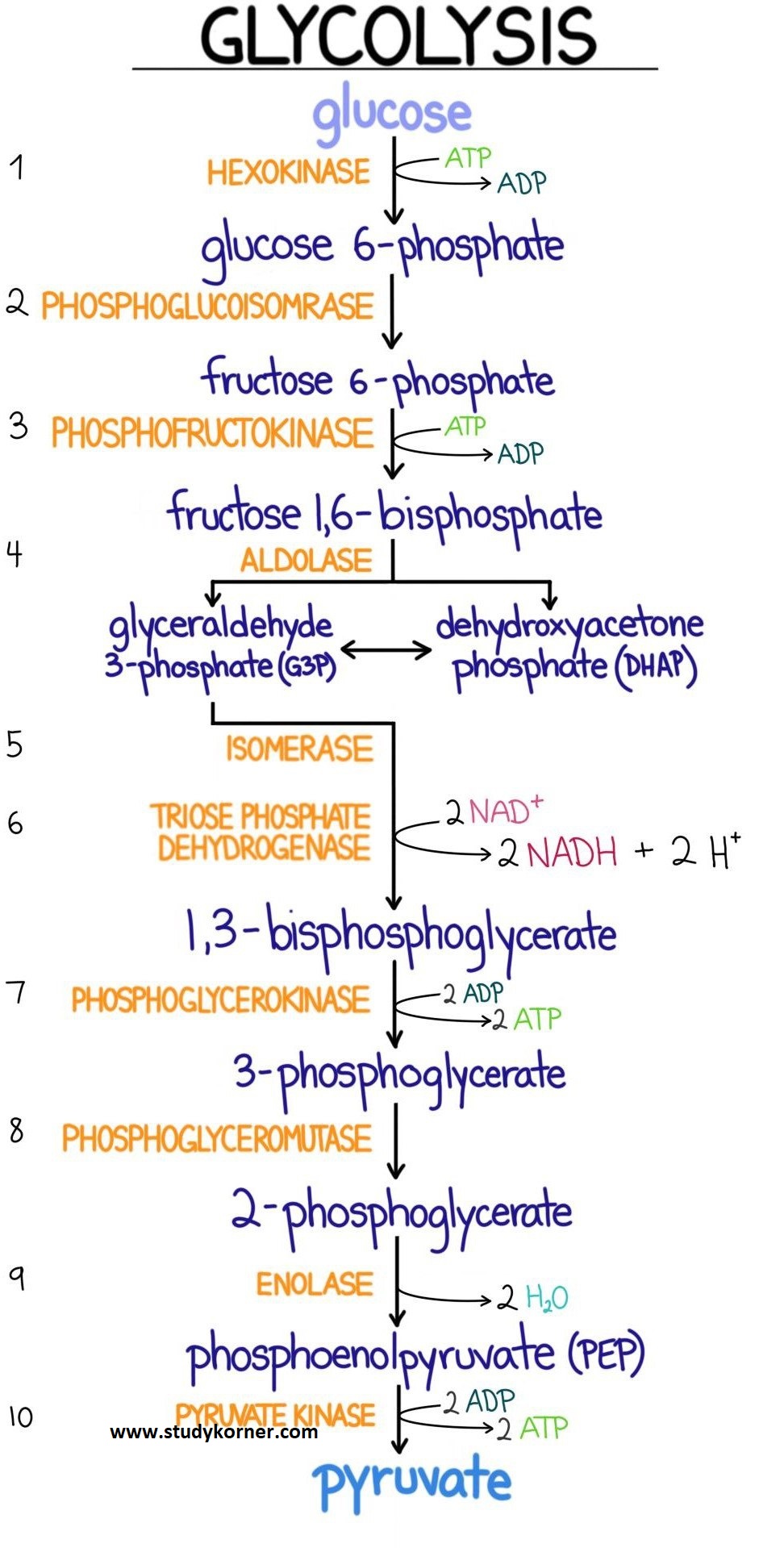
Stage 1 is the investment stage. 2 mols of atp are consumed for each mol of glucose. However, it is assumed as a linear pathway of ten enzyme meditation steps. Web equation of glycolysis. The 3 stages of glycolysis. What is the net gain of atp from one glucose molecule? Explain how cells cope with the lack of oxygen and inability of pyruvate (end product of glycolysis) to enter the tca cycle and how the process of anaerobic glycolysis continues. Where in the cell does glycolysis occur? The corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis. Web glycolysis is the process in which glucose is broken down to produce energy. Adp and nad stand for adenosine diphosphate and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, respectively. This leads to the synthesis of the ‘high energy’ intermediate molecules of atp and nadh. Glycolysis is a process in which glucose divided into two pyruvate molecules. Or lactate under anaerobic conditions along with the production of atp. Web glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol).
One Method Is Through Secondary Active Transport In Which The Transport Takes Place Against The Glucose Concentration Gradient.
Or lactate under anaerobic conditions along with the production of atp. The corresponding anabolic pathway by which glucose is synthesized is termed gluconeogenesis. Understand the 3 critical steps of glycolysis that are regulated and explain the significance of these three steps being regulated. Explain how cells cope with the lack of oxygen and inability of pyruvate (end product of glycolysis) to enter the tca cycle and how the process of anaerobic glycolysis continues.
The Following Equation Well Summarizes The Process Of Glycolysis:
However, it is assumed as a linear pathway of ten enzyme meditation steps. Web glycolysis is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose (c 6 h 12 o 6) into pyruvate and, in most organisms, occurs in the liquid part of cells (the cytosol). Web glycolysis takes place in the cytosol of a cell, and it can be broken down into two main phases: Web glycolysis is the metabolic process that serves as the foundation for both aerobic and anaerobic cellular respiration.
4.5/5 (12K Reviews)
Web imagine how you can connect steps of glycolysis to parts of the kreb’s cycle, or the pentose phosphate pathway. Glycolysis is a process in which glucose divided into two pyruvate molecules. C6h12o6 + 2adp + 2pi + 2nad+ → 2c3h4o3 + 2h2o + 2atp + 2nadh + 2h+ c6h12o6 is glucose and c3h4o3 is pyruvate. Web glycolysis is the essential starting point for glucose metabolism and energy generation in the cell.
Web Glycolysis Is The Process In Which Glucose Is Broken Down To Produce Energy.
Web glycolysis flow chart introduction pathway diagram & summary. Role of glycolysis in producing atps and nadhs and converting glucose to pyruvates. This leads to the synthesis of the ‘high energy’ intermediate molecules of atp and nadh. Why is glycolysis studied so extensively?