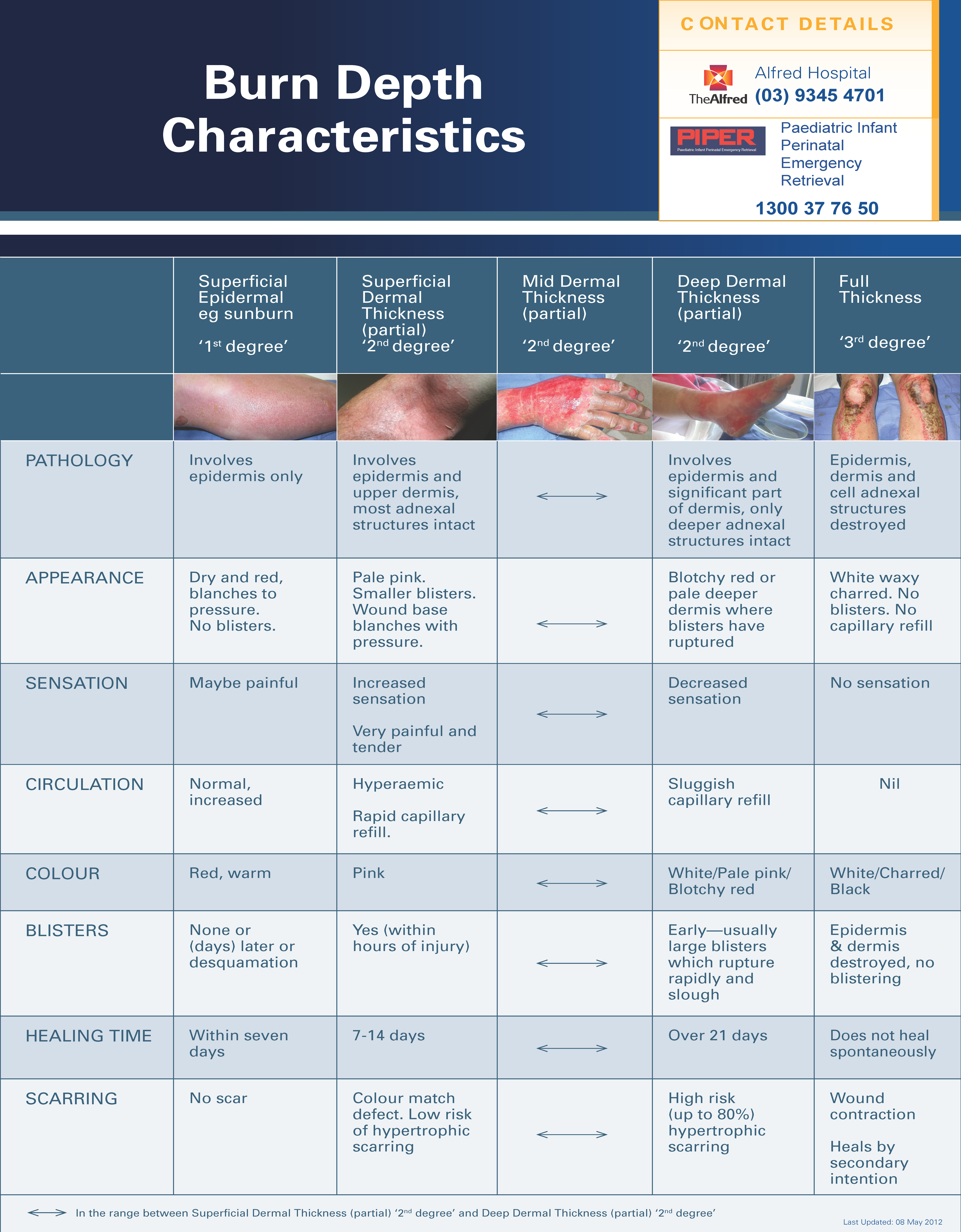
To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. (see treatment of minor thermal burns.) To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns. Al thickness) skin may be red, blistered, swollen. This practice guideline will outline the essential elements of.
To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. The extent of large tbsa burns is often underestimated, and factors such as sex, body shape,. Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue as a result of exposure to heat (eg, hot liquids [scalds], hot solids [contact burns], smoke [inhalation injury], or direct flames), ultraviolet/infrared radiation, radioactive materials, electricity, friction, chemicals, or. *areas of difference between the pediatric and adult population are represented by bold italics. Consequently, burns may be deeper and more severe than they initially appear (american burn association, 2018).
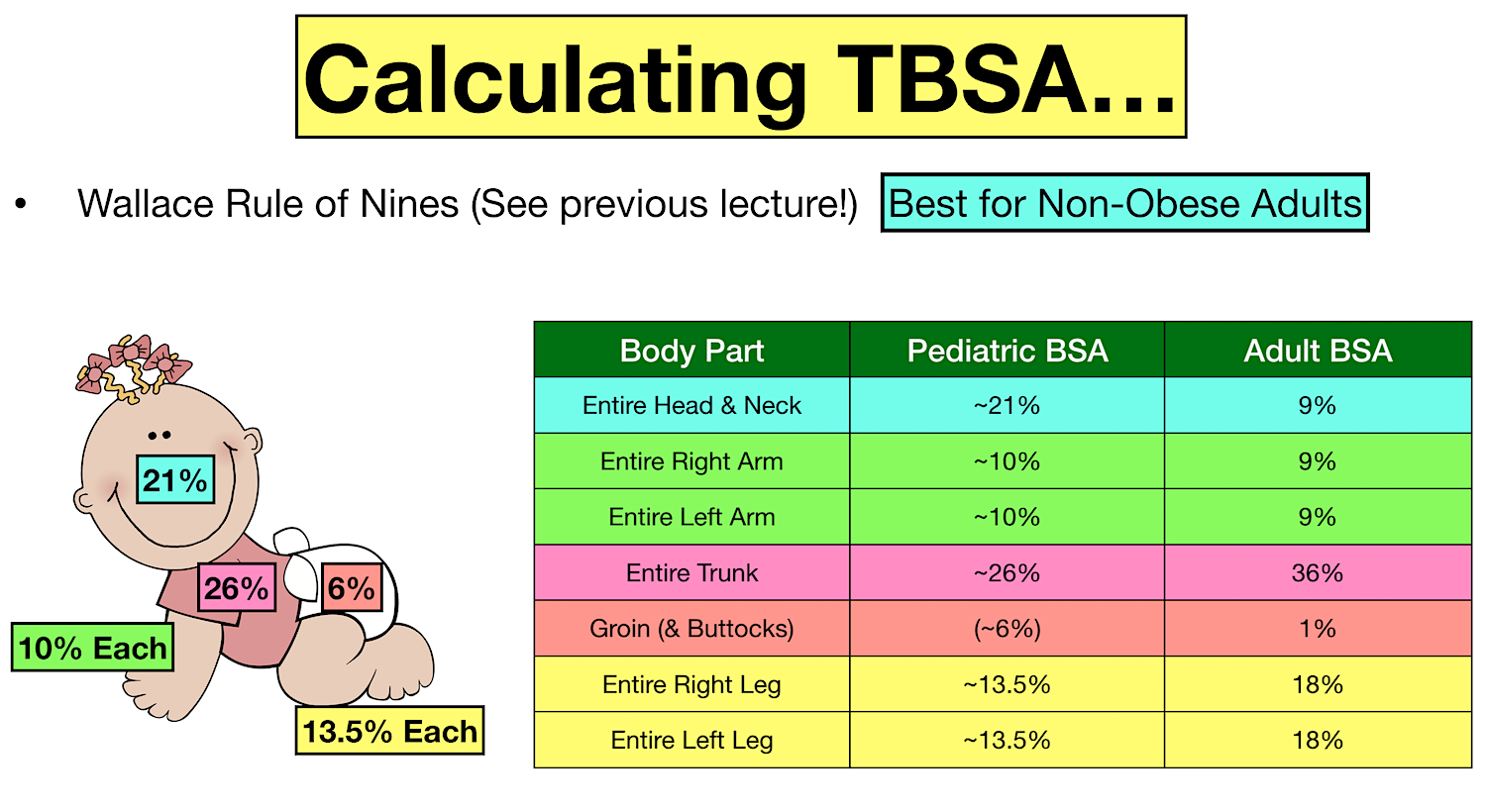
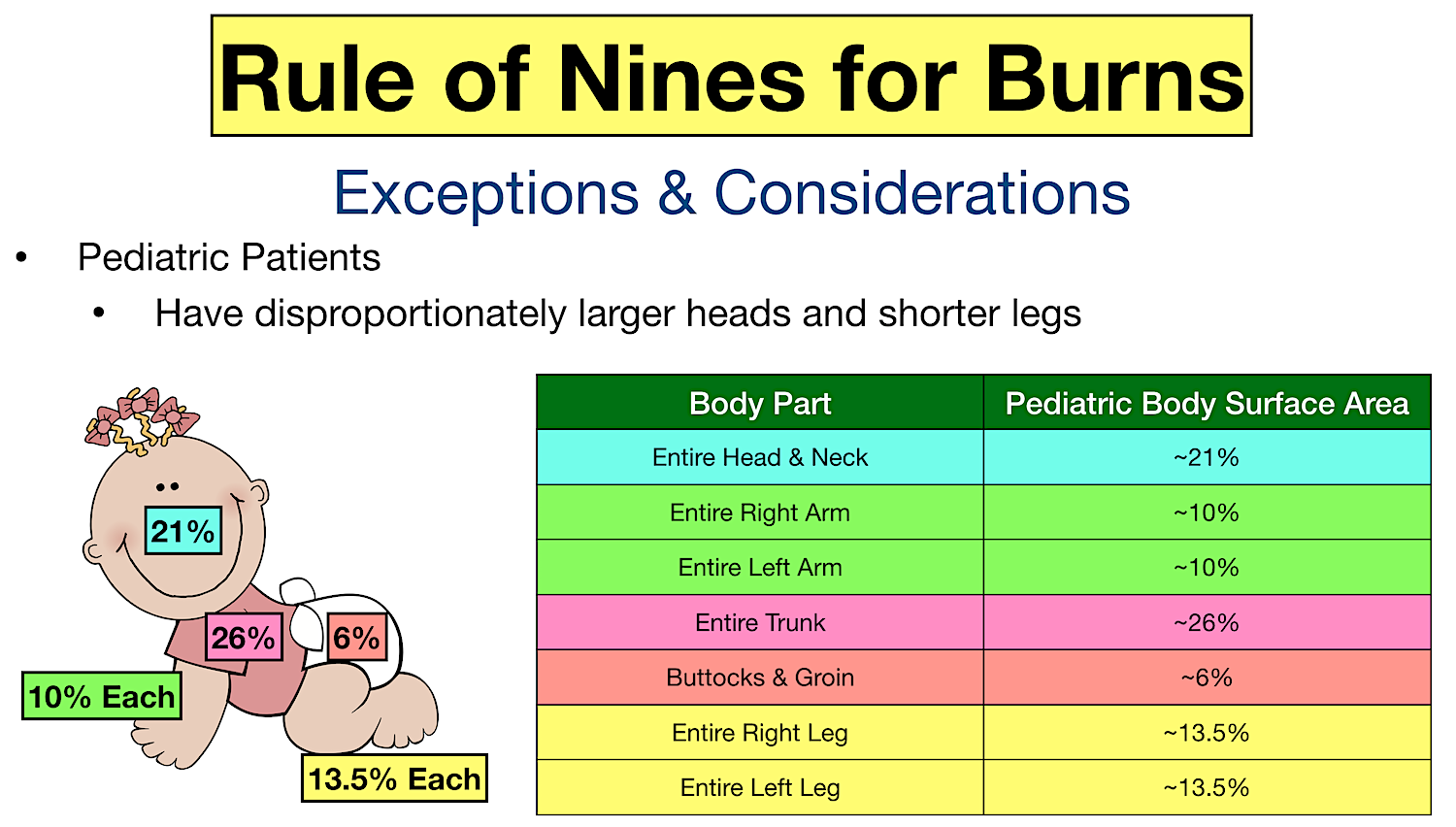
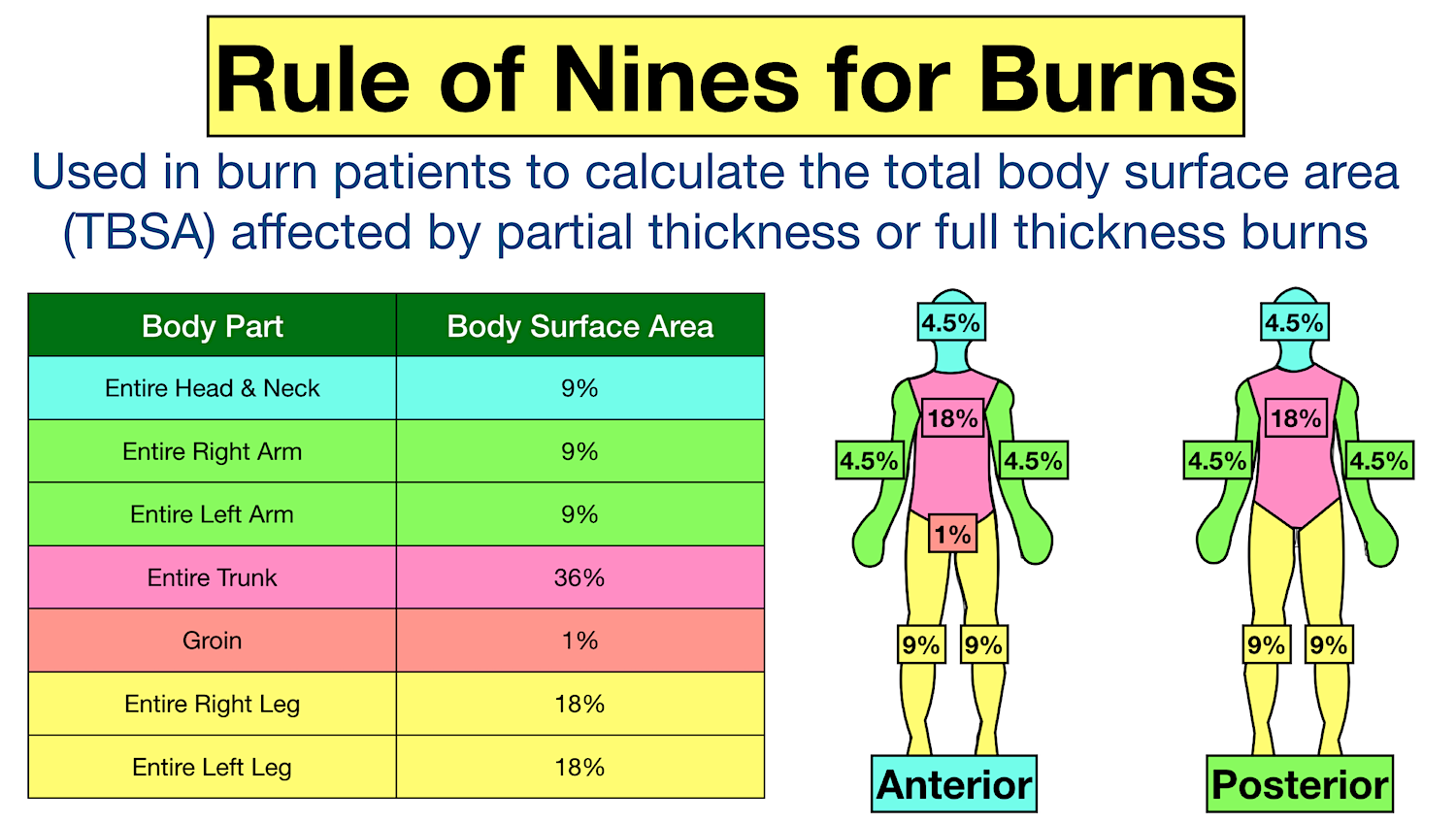
To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. Web burn total body surface area (tbsa) % for children. To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns. Al thickness) skin may be red, blistered, swollen. *infants and the elderly have thinner skin;
This practice guideline will outline the essential elements of. Web this topic will review the emergency management of moderate to severe thermal burns in children ( table 1 ). To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. Web learn to calculate pediatric burned surface area with the rule of nines on the web's most interactive pediatric rule of nines learning tool. Al thickness) skin may be red, blistered, swollen. The care of minor thermal burns, smoke inhalation, chemical burns to the skin and eye, electrical injuries, and ongoing burn management, are discussed separately. *infants and the elderly have thinner skin; The extent of large tbsa burns is often underestimated, and factors such as sex, body shape,. To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns. Roughly 25% of all burn injuries occur in children under the age of 15 years. Web burn total body surface area (tbsa) % for children. Web what is a clinical pathway? Web infant/pediatric lund and browder burn chart. Web explain the benefits of providing optimal sedation and analgesia for children having burns procedures outside the operating theatre, and the drugs commonly used. Consequently, burns may be deeper and more severe than they initially appear (american burn association, 2018).
Consequently, Burns May Be Deeper And More Severe Than They Initially Appear (American Burn Association, 2018).
This practice guideline will outline the essential elements of. The extent of large tbsa burns is often underestimated, and factors such as sex, body shape,. Web burn total body surface area (tbsa) % for children. Al thickness) skin may be red, blistered, swollen.
*Areas Of Difference Between The Pediatric And Adult Population Are Represented By Bold Italics.
To appropriately triage, diagnose and classify burns in the pediatric patient. Web what is a clinical pathway? *infants and the elderly have thinner skin; Web explain the benefits of providing optimal sedation and analgesia for children having burns procedures outside the operating theatre, and the drugs commonly used.
Roughly 25% Of All Burn Injuries Occur In Children Under The Age Of 15 Years.
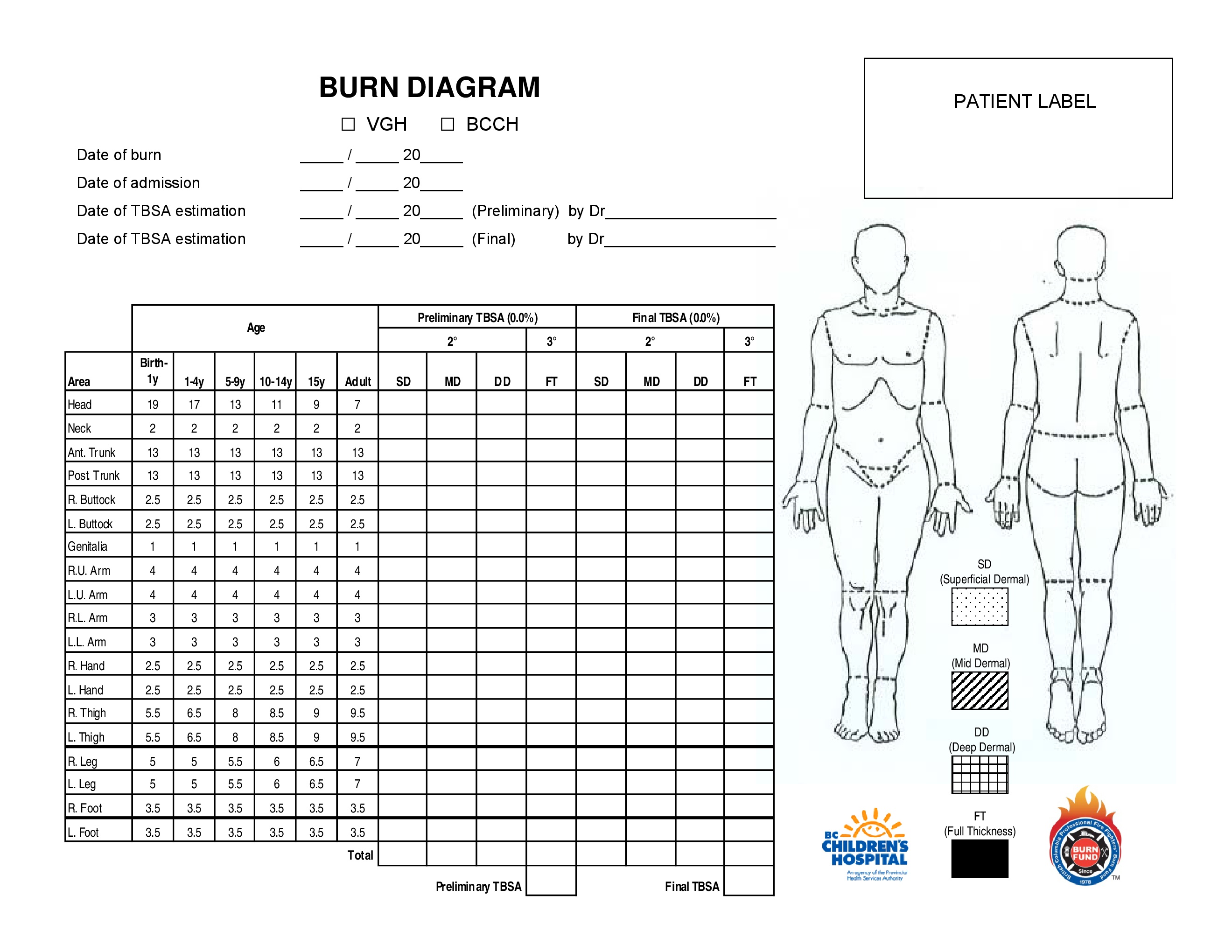
Web this topic will review the emergency management of moderate to severe thermal burns in children ( table 1 ). Web learn to calculate pediatric burned surface area with the rule of nines on the web's most interactive pediatric rule of nines learning tool. (see treatment of minor thermal burns.) Web infant/pediatric lund and browder burn chart.
The Care Of Minor Thermal Burns, Smoke Inhalation, Chemical Burns To The Skin And Eye, Electrical Injuries, And Ongoing Burn Management, Are Discussed Separately.
Web pediatric burns are injuries to the skin or other tissue as a result of exposure to heat (eg, hot liquids [scalds], hot solids [contact burns], smoke [inhalation injury], or direct flames), ultraviolet/infrared radiation, radioactive materials, electricity, friction, chemicals, or. To decrease variability in the management of patients with burns.