Web sediment in the urine happens when crystals, bacteria, or blood exit through the urine. Urine analysis can provide useful information about your health. Picture of urine dipstick and color box instructions; Web cells found in urine. Many conditions can cause urinary sediment.
Well as those with proteinuria, hematuria, and leukocyturia identified on dipstick urinalysis. Normal urine usually contains traces of invisible sediment or particles that can only show up in a urinalysis. In many cases, sediment can only be detected by a clinical test such as a urinalysis. Picture of urine dipstick and color box instructions; Web sediment in urine refers to gritty particles, mucus, white or red blood cells, that can be detected in a urine test or that give urine a cloudy look.
When the body lacks sufficient water, urine becomes more concentrated with salts, minerals, and other substances, which can precipitate out as visible particles. Sediment in the urine can have many causes. Cloudy urine is generally harmless but frequent and repetitive cloudy urine could be. Web sediment in the urine happens when crystals, bacteria, or blood exit through the urine. Web doctors & departments.
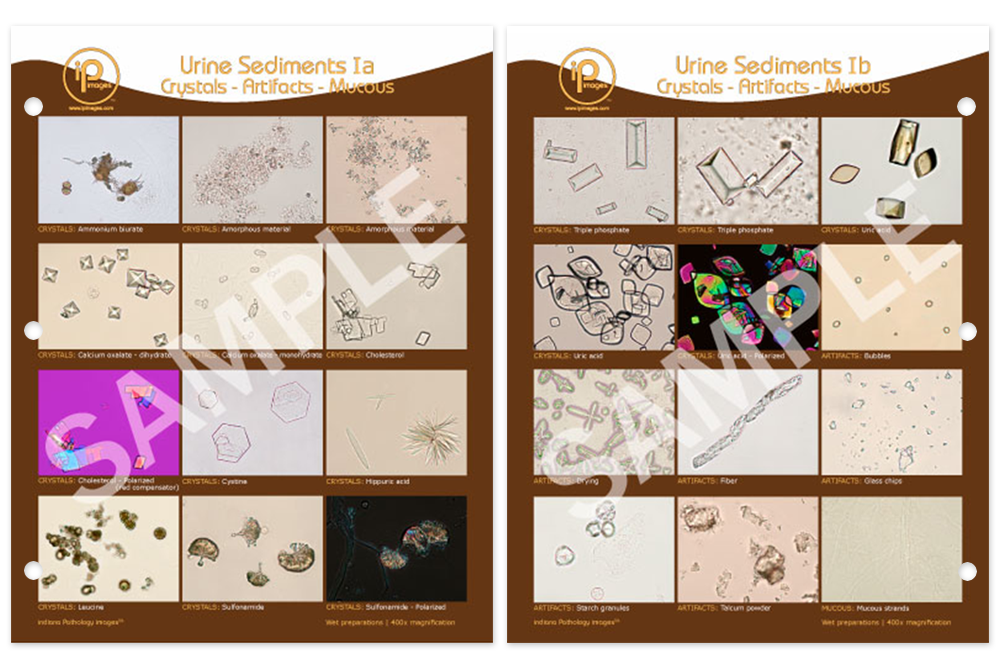
Following the format of the previous cap color atlases, the text includes photomicrographs of the urinary sediment, a discussion of the pertinent morphologic features of each element, and the results of the identification of the particular element by both. Epithelial cells three types of epithelial cells may appear in urine sediment: Web the color of urine can help identify whether a person is hydrated. It can also provide an indication of underlying medical conditions. Web when used properly, urine sediment findings alert health care providers to the presence of kidney disease, while also providing diagnostic information that often identifies the compartment of kidney injury. Web doctors & departments. Cloudy urine occurs when your urine has a hazy or milky color that is not a normal, clear, light yellow. Renal tubular, transitional, and/or squamous. In many cases, sediment can only be detected by a clinical test such as a urinalysis. Figure 2 from cavanaugh and perazella, ajkd, © national kidney foundation. Normal urine usually contains traces of invisible sediment or particles that can only show up in a urinalysis. Picture of urine dipstick and color box instructions; Normal values are as follows: Web learn what kinds of things urine tests check for, plus normal and abnormal ranges and what they might indicate. Web urine sediment examination should utilize 5 ml of fresh urine.
Web Uncomplicated Urinary Tract Infections Diagnosed By Positive Leukocyte Esterase And Nitrite Tests Can Be Treated Without Culture.
However, it is more important that technicians are consistent when obtaining and evaluating the urine than the amount of urine obtained. Web sediment in the urine happens when crystals, bacteria, or blood exit through the urine. Web the color of urine can help identify whether a person is hydrated. They learn to interpret results and correlate with.
A Urinalysis Involves Checking The Appearance, Concentration And Content Of Urine.
Cloudy urine occurs when your urine has a hazy or milky color that is not a normal, clear, light yellow. When the body lacks sufficient water, urine becomes more concentrated with salts, minerals, and other substances, which can precipitate out as visible particles. A urinalysis is simply an analysis of the urine. Epithelial cells three types of epithelial cells may appear in urine sediment:
Urinalysis Is Invaluable In The Diagnosis Of Urologic.
Cloudy urine is generally harmless but frequent and repetitive cloudy urine could be. In addition, abnormal findings on a routine urinalysis, even in an otherwise asymptomatic patient, may be the first evidence of underlying kidney disease. Web doctors & departments. Web sediment in urine refers to gritty particles, mucus, white or red blood cells, that can be detected in a urine test or that give urine a cloudy look.
It Can Also Provide An Indication Of Underlying Medical Conditions.
Web in conjunction with the history, physical examination, and laboratory testing, the urinalysis plays a central role in evaluating acute and chronic kidney disease. Normal urine usually contains traces of invisible sediment or particles that can only show up in a urinalysis. Urine sediment findings may also guide therapy and assist in prognostication. Web when used properly, urine sediment findings alert health care providers to the presence of kidney disease, while also providing diagnostic information that often identifies the compartment of kidney injury.